Effect of Gabapentin on nerve conduction studies in carpal tunnel syndrome
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v5i1.406Keywords:
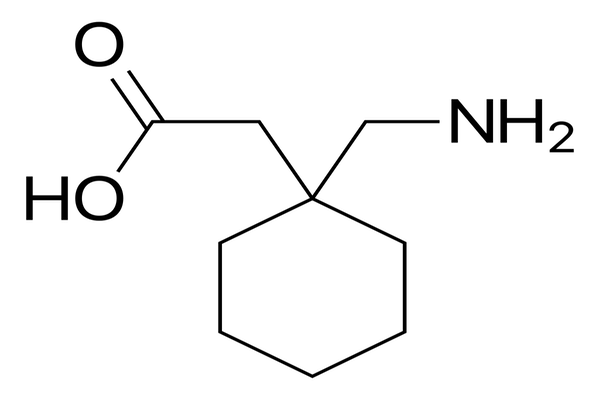
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, Gabapentin, Naproxen, Nerve Conduction StudyAbstract
Background: The most common type of neuropathy in adults is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) which is caused by compression of the median nerve at the wrist.
Methods: This quasi-experimental study was conducted to determine the efficacy of gabapentin on nerve conduction studies in patients with mild CTS. The patients with mild CTS were randomly allocated into two groups. Group A received naproxen alone (500 mg/day, orally) while group B received both gabapentin (100-300 mg) and naproxen (500 mg/day, orally) for two months. Sensory nerve conduction velocity (SNCV) and distal motor latency (DML) were performed at baseline and two months after treatment.
Results: There were no significant differences between the two groups with regards to the outcome parameters before initiation of intervention. The SNCV and DML showed no significant improvements in group A (p>0.05), whereas for group B the SNCV and DML of the median nerve were significantly improved at two months after treatment (p<0.001).
Conclusion: Gabapentin was found to be effective for SNCV and DML in patients with mild CTS over a two-month period.
References
Deniz, O., Aygül, R., Kotan, D., Ozdemir, G., Odabaş, F. O., Kaya, M. D., & Ulvi, H. (2012). The effect of local corticosteroid injection on F-wave conduction velocity and sympathetic skin response in carpal tunnel syndrome. Rheumatology International, 32(5), 1285–1290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-010-1772-z PMID:21274539
Eftekharsadat, B., Babaei-Ghazani, A., & Habibzadeh, A. (2015). The Efficacy of 100 and 300 mg Gabapentin in the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 14(4), 1275–1280. PMID:26664397
Evcik, D., Kavuncu, V., Cakir, T., Subasi, V., & Yaman, M. (2007). Laser therapy in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized controlled trial. Photomedicine and Laser Surgery, 25(1), 34–39. https://doi.org/10.1089/pho.2006.2032 PMID:17352635
Gurcay, E., Unlu, E., Gurcay, A. G., Tuncay, R., & Cakci, A. (2009). Evaluation of the effect of local corticosteroid injection and anti-inflammatory medication in carpal tunnel syndrome. Scottish Medical Journal, 54(1), 4–6. https://doi.org/10.1258/rsmsmj.54.1.4 PMID:19291926
Heybeli, N., Kutluhan, S., Demirci, S., Kerman, M., & Mumcu, E. F. (2002). Assessment of outcome of carpal tunnel syndrome: A comparison of electrophysiological findings and a self-administered Boston questionnaire. Journal of Hand Surgery (Edinburgh, Lothian), 27(3), 259–264. https://doi.org/10.1054/jhsb.2002.0762 PMID:12074615
Hui, A. C., Wong, S., Leung, C. H., Tong, P., Mok, V., Poon, D., . . . Boet, R. (2005). A randomized controlled trial of surgery vs steroid injection for carpal tunnel syndrome. Neurology, 64(12), 2074–2078. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.WNL.0000169017.79374.93 PMID:15985575
Hui, A. C., Wong, S. M., Leung, H. W., Man, B. L., Yu, E., & Wong, L. K. (2011). Gabapentin for the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized controlled trial. European Journal of Neurology, 18(5), 726–730. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2010.03261.x PMID:21143704
Huisstede, B. M., Hoogvliet, P., Randsdorp, M. S., Glerum, S., van Middelkoop, M., & Koes, B. W. (2010). Carpal tunnel syndrome. Part I: Effectiveness of nonsurgical treatments—a systematic review. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 91(7), 981–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2010.03.022 PMID:20599038
Ibrahim, I., Khan, W. S., Goddard, N., & Smitham, P. (2012). Carpal tunnel syndrome: A review of the recent literature. The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 6(1), 69–76. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874325001206010069 PMID:22470412
Jin, G. Q., Yang, J., Li, C. Y., Ming, X. F., Zhao, X. F., & Cheng, C. S. (2012). [Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome with mini-incision decompression]. Zhongguo Gu Shang, 25(1), 58–61. PMID:22489526
Karadaş, O., Omaç, O. K., Tok, F., Ozgül, A., & Odabaşi, Z. (2012). Effects of steroid with repetitive procaine HCl injection in the management of carpal tunnel syndrome: An ultrasonographic study. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 316(1-2), 76–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2012.01.023 PMID:22336701
Nicholson, B. (2000). Gabapentin use in neuropathic pain syndromes. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica, 101(6), 359–371. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0404.2000.0006a.x PMID:10877151
Ono, S., Clapham, P. J., & Chung, K. C. (2010). Optimal management of carpal tunnel syndrome. International Journal of General Medicine, 3, 255–261. PMID:20830201
Padua, L., LoMonaco, M., Gregori, B., Valente, E. M., Padua, R., & Tonali, P. (1997). Neurophysiological classification and sensitivity in 500 carpal tunnel syndrome hands. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica, 96(4), 211–217. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0404.1997.tb00271.x PMID:9325471
Sabet, R., Rahmanian, K., Jahromi, A.S., and Madani, A. (2017). Analgesic effect of gabapentin in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science Vol 7, 079-082.
Serpell, M. G., & the Neuropathic pain study group. (2002). Gabapentin in neuropathic pain syndromes: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pain, 99(3), 557–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3959(02)00255-5 PMID:12406532
Taverner, D., Lisbona, M. P., Segalés, N., Docampo, E., Calvet, J., Castro, S., & Benito, P. (2008). [Efficacy of gabapentin in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome]. Medicina Clínica, 130(10), 371–373. https://doi.org/10.1157/13117468 PMID:18381028
Taylor, C.P., Gee, N.S., Su, T.Z., Kocsis, J.D., Welty, D.F., Brown, J.P., Dooley, D.J., Boden, P., and Singh, L. (1998). A summary of mechanistic hypotheses of gabapentin pharmacology. epilepsy research 29, 233-249.
Tseng, C. H., Liao, C. C., Kuo, C. M., Sung, F. C., Hsieh, D. P., & Tsai, C. H. (2012). Medical and non-medical correlates of carpal tunnel syndrome in a Taiwan cohort of one million. European Journal of Neurology, 19(1), 91–97. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2011.03440.x PMID:21631646
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
