Inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: A friend or foe?
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v5i8.464Keywords:
Alzheimers disease, beta amyloid, Inflammation, Proinflammatory cytokines, TauAbstract
Background: There is a dearth of precise information for molecular and cellular mechanisms responsible for the development of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, convincing data from clinical research and basic molecular biology have shown that inflammation of the brain is an integral part of AD. In this review, the role of inflammation in AD will be highlighted.
Methods: Articles from credible scientific databases, such as ScienceDirect, Scopus, PubMed, Google Scholar and Mendeley, were searched and retrieved using keywords ‘inflammation’, ‘Alzheimer’s disease’, ‘tau’, and ‘beta amyloid’.
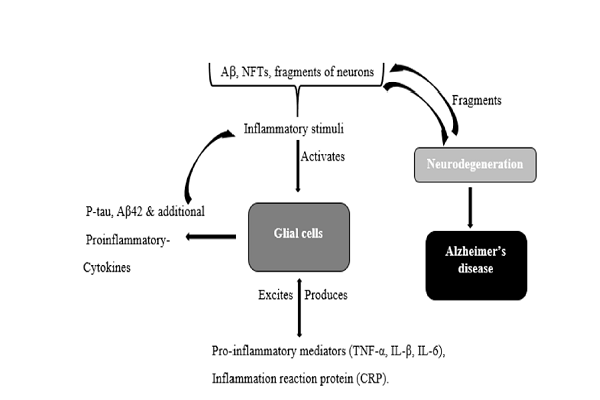
Results: At present, there is no local inflammatory-inciting factor that is closely associated with AD, although it has been proposed that inflammation could be induced by pathologic hallmarks of AD, such as beta amyloid (Aβ) peptide plagues and neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), or fragments of degenerated neurons. However, it is still unclear whether inflammation leads to the development of AD or if the pathological hallmarks of AD induce inflammation.
Conclusion: Inflammation is, indeed, an integral part of AD. Further studies on inflammatory-targeted therapies for AD are highly recommended.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
