Molecular detection of virulence genes in Klebsiella Pneumoniae clinical isolates from Kurdistan Province, Iran
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v5i8.467Keywords:
entB, iutA, K2, kfu, Klebsiella pneumoniae, magA, mrkD, rmpA, ybtSAbstract
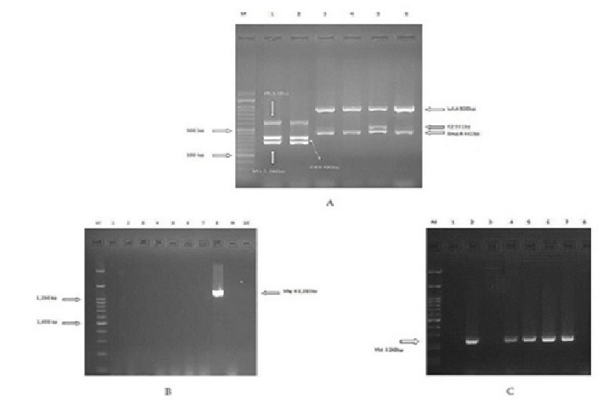
Introduction: The purpose of this study was to detect ybtS, entB, mrkD, magA, kfu, iutA, rmpA and K2 genes in extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) - and non-ESBL producing Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Methods: To this end, 70 K. pneumoniae isolates were selected from hospitals of Kurdistan Province, Iran. The ESBL phenotype was conducted utilizing the disc diffusion technique in accordance with CLSI procedures. Detection of virulence factor genes was performed by the PCR in the ESBL and non-ESBL isolates.
Results: Sixty-two (88.6%) isolates of K. pneumoniae were ESBL producers. Further, entB had the most frequency in all the isolates. There were no significant differences between ESBL production and the presence of ybt S, entB, mrkD, magA, kfu, iutA, rmpA and K2 genes and the presence of these genes and variables such as presence of sex, clinical specimen type, and hvKP phenotype among the ESBL and non-ESBL K. pneumoniae isolates.
Conclusion: In conclusion, in other studies, K. pneumoniae strains were separated from liver abscesses and the magA gene was frequently present; however, in our study, the K. pneumoniae strains were separated from various clinical specimens and the magA gene had low frequency.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
