The therapeutic effectiveness of sitagliptin with niacin and chromium picolinate on glycosylated hemoglobin in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v5i8.469Keywords:
B3, CrPlt, FBS, HbA1c, Niacin, RBS, T2DMAbstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of niacin (B3) on glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), alone and as adjunct therapy, with chromium picolinate (CrPlt) and sitagliptin. In the present study, we have evaluated the effects of niacin and chromium picolinate supplementation with sitagliptin in Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients.
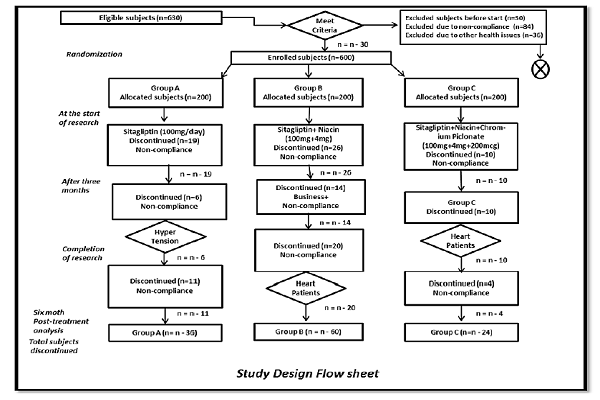
Methods: A randomized controlled trial was conducted on 600 patients suffering from T2DM from four different hospitals in Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan; patients were divided into three groups (n=200 per group). Group A was given sitagliptin (100 mg), Group B received niacin (14 mg/d) along with sitagliptin, and Group C received chromium picolinate (200 mcg/d) and niacin (14 mg/d) along with sitagliptin, for a duration of 6 months. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare the efficacy of all treatment groups, and statistical significance was set at p≤0.05.
Results: The data indicated that all defined therapies have a significant influence with respect to fasting blood sugar (FBS) (p<0.0001), random blood sugar (RBS) (p<0.0001) and glycosylated hemoglobin (p<0.0001).
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that low doses of niacin and chromium picolinate supplementation with sitagliptin helps in maintaining glycemic control in patients with T2DM, and provides the best treatment option among those considered.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
