Hypoalgesic effect of Spirulina platensis on the sciatic neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury in male rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v5i9.477Keywords:
Chronic constriction injury, Neuropathic pain, Oxidative stress, Rat, Spirulina platensisAbstract
Background: It has been revealed that herbal medicines have a palliative effect on pain. In the present study, the hypoalgesic effect of Spirulina platensis (microalgae) on the neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury (CCI) was investigated.
Methods: In the present study, 74 adult male Wistar rats weighing 200-220 grams were used. For inducing neuropathic pain, CCI was performed on the left sciatic nerve. Spirulina platensis was intragastrically administered daily for 3 weeks. Mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia were assessed by Von Frey hairs and plantar test device, respectively. Malondialdehyde (MDA) and total antioxidant capacity (TOC) were detected in the serum using thiobarbituric acid and ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP), respectively.
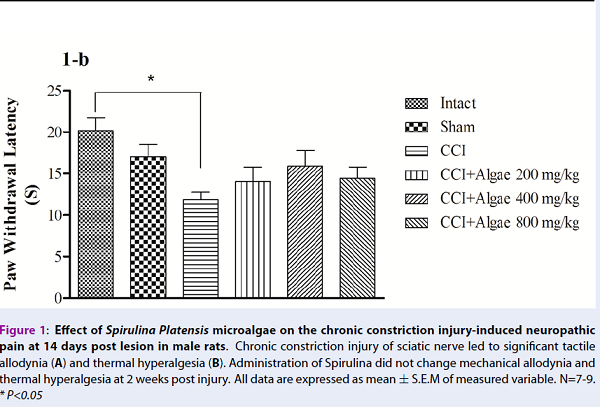
Results: CCI of the sciatic nerve led to mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia at three weeks as well as two weeks post surgery. Three weeks of Spirulina therapy significantly (P<0.05) decreased paw withdrawal response to mechanical and thermal stimulations, compared to control. FRAP, but not MDA, significantly decreased three weeks after CCI, and Spirulina therapy significantly reversed its level towards control.
Conclusion: Chronic intragastric administration of Spirulina platensis alleviates CCI-induced neuropathic pain by modulating oxidative stress through increasing FRAP levels in male rats.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
