Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of Amygdalus eburnea shell root extract in mice
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v5i10.489Keywords:
Hot-plate, Inflammation, Mice, Pain, Rotarod, Tail-flickAbstract
Introduction: The current study aims to assess the antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of Amygdalus eburnea Spach extract in mice.
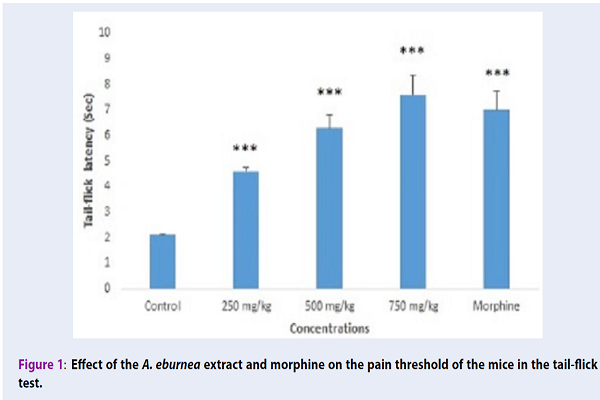
Methods: Totally, 114 NMRI mice were used in this study. The acute toxicity was evaluated for two days. The antinociceptive effect was accessed by using the hot-plate, tail-flick, and rotarod test. In this investigation, anti-inflammatory effects were evaluated by using the Xylene-induced ear edema method. The findings demonstrated that in the hot-plate and tail-flick tests, A. eburnea extract particularly at the dose of 750 mg/kg demonstrated a considerable analgesic effect; so that there was a significant difference between the extract-treated group and the control group (p<0.05).
Results: The results showed that the administration of A. eburnea extract especially at the dose of 500 and 750 mg/kg significantly decreased the ear edema induced by xylene in comparison to the control group. There was no significant difference after injecting of various doses of A. eburnea extract in the sensory-motor test (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: These results demonstrated the potent antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of A. eburnea extract in mice. Nevertheless, the precise mechanisms responsible for these activities remain to be studied.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
