The effects of Matricaria chamomilla L.hydroalcoholic extract on atherosclerotic plaques, antioxidant activity, lipid profile and inflammatory indicators in rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v5i10.490Keywords:
Antioxidant activity, Atherosclerotic plaques, Inflammatory markers, Lipid profile, Matricaria chamomilla L., RatsAbstract
Introduction: Treatment of cardiovascular risk factors seems to be necessary and involves a number of changes in drug treatment and lifestyle. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of Matricaria chamomilla L. hydroalcoholic extract on antioxidant activity, atherosclerotic plaques, lipid profile and inflammatory indicators in rats.
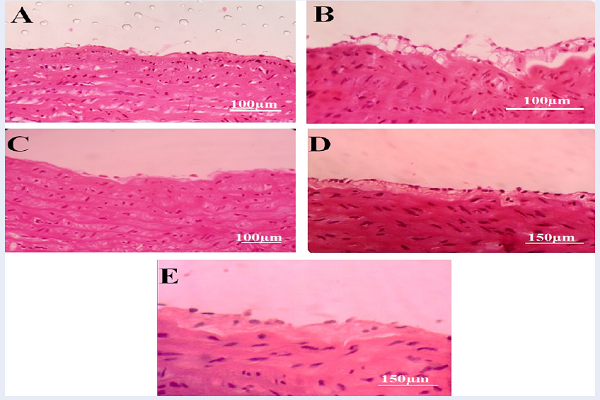
Methods: Thirty male Wistar rats were divided into five experimental groups consisting of group 1 (Sham; normal dietary), group 2 (control; high cholesterol diet (2%)), group 3 (high cholesterol diet plus 55 mg/kg of chamomile hydroalcoholic extract), group 4 (high cholesterol diet plus 110 mg/kg of chamomile hydroalcoholic extract), and group 5 (high cholesterol diet plus 10 mg/kg of lovastatin). At the beginning and end of the study, blood samples of all the animals were taken for determination of antioxidant activity and the level of biochemical parameters. The hearts and aorta were also isolated for ontological tests.
Results: No symptom of plaque formation was observed in experimental groups 3, 4 and 5 that received the high cholesterol diet. High cholesterol diet (2%) resulted in a significant increase in serum cholesterol level, TG and LDL-c levels in groups 2 and 3 as compared to group 1 (P<0.001). No significant difference was observed in serum cholesterol, TG and LDL-c levels in experimental groups 4 and 5, compared to experimental group 1. In group 4, serum HDL-c concentration did not show significant changes as compared to group 1. In groups 4 and 5, no significant change was observed in inflammatory factors as compared to group 1. The levels of superoxide dismutase in red blood cells and malondialdehyde in plasma of groups 3 and 5 showed no significant change when compared with group 1.
Conclusion: Chamomile led to the management and correction of changes in risk factors of cardiovascular diseases.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
