Efficacy of topical cinnamon gel for the treatment of facial acne vulgaris: A preliminary study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v6i1.515Keywords:
Acne vulgaris, Cinnamon, Red fluorescence spot, Skin biophysical profileAbstract
Background: Acne vulgaris is a common chronic disorder of the pilosebaceous unit. Topical therapy is the mainstay of treatment for mild-to-moderate acne. Two main problems with conventional anti-acne treatments are antibiotic resistance and local side effects. In this regard, medicinal herbs could be an alternative choice for developing new products with fewer side effects. Objective: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a topical formulation of cinnamon in patients with facial acne.
Method: In this open-label, assessor-blind, and uncontrolled clinical trial, 20 patients (18F/2M) with mild-to-moderate facial acne were treated with topical cinnamon gel twice-daily for eight weeks. The outcomes of acne lesion count, red fluorescence parameters and skin biophysical profile were evaluated at baseline, 4th and 8th week. For safety assessment, any adverse drug reaction was recorded during the study.
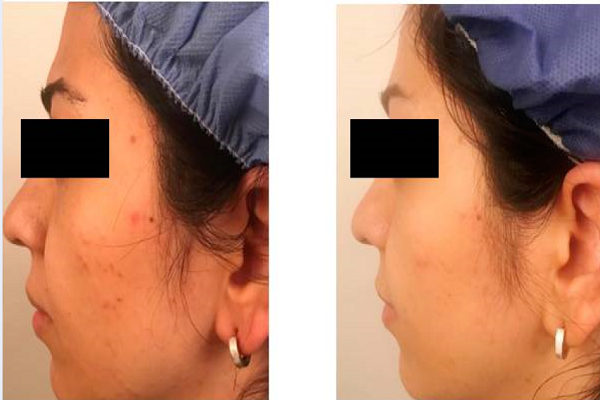
Results: Two months after using cinnamon gel, there was a significant reduction in the total (47%, p=0.000), inflammatory (42%, p=0.026), and non-inflammatory (48%, p=0.002) lesion count. Also, the size of red fluorescence spots was significantly reduced (p<=0.05). In skin biophysical measurement, there was a significant decrease in erythema (61.31+/-68.25), sebum (31.05+/-36.15), and hydration (10.05+/-10.16), as well as a significant increase in pH (0.63+/-0.75). Some patients experienced mild, transient erythema and burning immediately after applying the gel, but no serious side effects were reported.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that topicalcinnamongel is efficient and safe for the treatment of mild-to-moderate facial acne.
IRCT registration code: IRCT2016031126938N3
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
