Effect of Thalidomide on Cox-2 expression in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v6i1.518Keywords:
Bleomycin, Cyclooxygenase 2, Lung fibrosis, Mice, ThalidomideAbstract
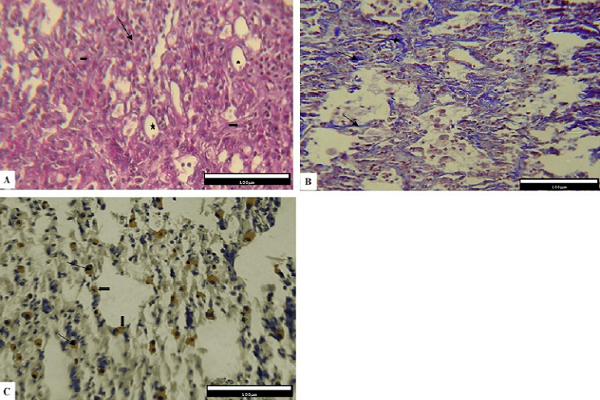
Introduction: Lung fibrosis is a progressive, fatal disease that is characterized by increasing fibroblasts proliferation and extracellular matrix precipitation. Studies have shown that cyclooxygenase- 2 (Cox-2) could play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of lung fibrosis. In the current study, the effect of thalidomide on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis was qualitatively studied in a laboratory animal model.
Methods: Thirty-two adult male C57BL/6 mice were randomly assigned to the following four groups: Group one received 2 mg bleomycin, group two received bleomycin in addition to 4 mg of thalidomide; group three received 4 mg of thalidomide, and Group 4 received 0.1 mg of 0.5% carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) via intraperitoneal (IP) administration. Finally, the expression of Cox-2 protein and the percentage of contact points of alveolar spaces and pulmonary connective tissue were determined.
Results: Our results showed that in the Bleo + Thal group compared to the Bleo group, the percentage of contact points of pulmonary connective tissue decreased significantly (P<0.001), while the percentage of contact points among the alveolar spaces increased significantly (P = 0.01). Also, immunohistochemical studies have demonstrated the number of Cox-2+ cells in the volume unit in the Bleo + Thal group decreased significantly in comparison with the group that received only Bleo (P = 0.012).
Conclusion: In conclusion, these results suggest thalidomide could alleviate the bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis and decreases the expression of Cox-2 protein.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
