Comparison of biomarkers between genotypes 1a and 3a in hepatitis C virus patients with control group
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v6i4.537Keywords:
Biochemical markers, Genotype 1a, Genotype 3a, Hepatitis C Virus, Lipid profiles, Liver enzymes, Photometric methodAbstract
Introduction: Three percent of people worldwide are infected with Hepatitis C virus (HCV). A few studies have been performed to evaluate the biochemical markers of the disease. In the current study, biochemical markers were evaluated in HCV patients and the control group.
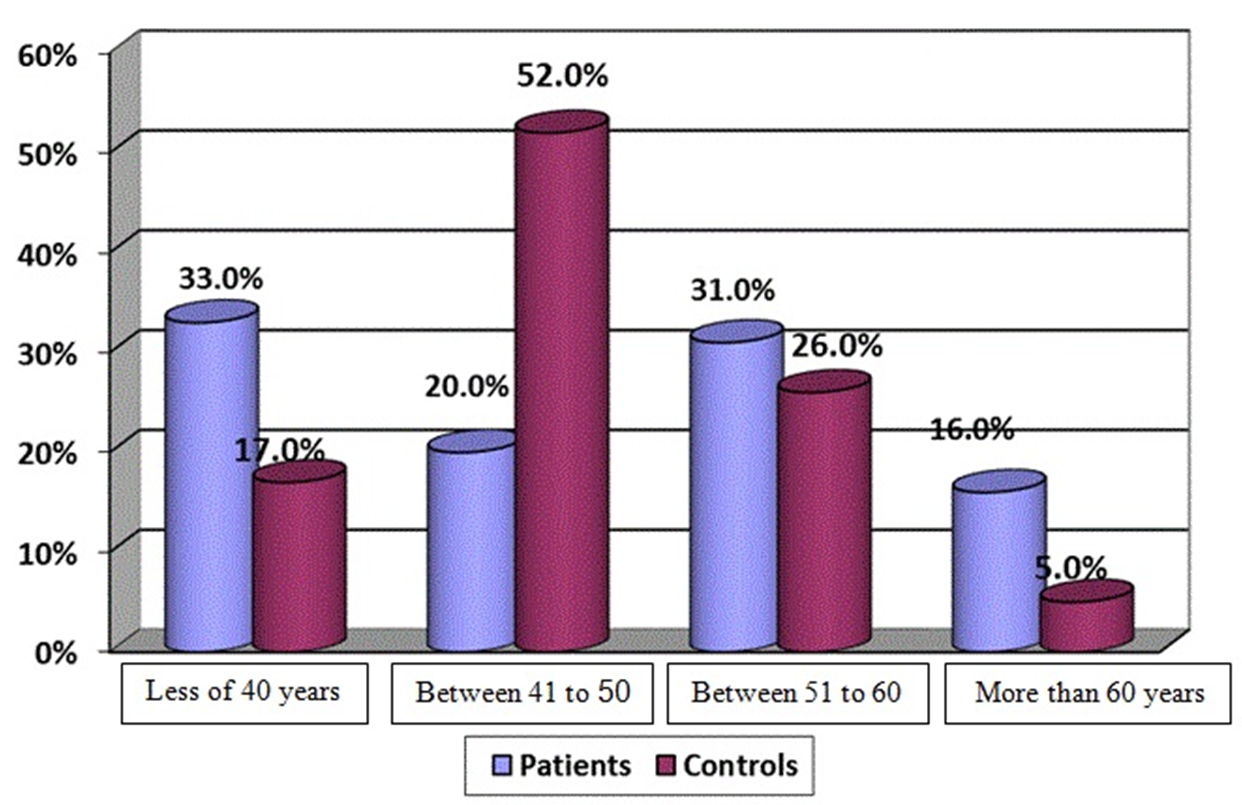
Methods: Two sex- and age-matched healthy individuals (n = 100) and HCV positive patients (n = 100) were included (mean age of 20-75, 26.0% females and 74.0% males). Biochemical markers, including liver enzymes (ALT, AST and ALP), lipid profiles (cholesterol, LDL, and HDL) and triglyceride (TG) were investigated in both groups. HCV genotyping was also performed by Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and OHNO methods.
Results: The biochemical markers between HCV patients and controls were compared (cholesterol, ALP, AST, ALT, LDL: p = 0.0001, HDL: p = 0.002, TG: p = 0.003), and statistically significant difference was found between two groups. The biochemical markers between HCV patients and the control group in terms of age was compared and no differences was observed (p = 0.741), however, there was a significant difference in sex between HCV patients and control group (26.0% females, 74.0% males in control group, and x% females and y% males in HCV patients) (p = 0.032). The results of HCV genotyping showed that 39 patients were genotype 1a, and 43 patients were genotype 3a, and 1 patient was genotype 2a. Evaluation of biochemical markers in patients with genotype 1a and 3a showed that there were significant differences in cholesterol (p = 0.001), LDL (p = 0.001) and HDL (p= 0.003) levels, but there were no significant differences in liver enzymes and TG levels in both genotypes.
Conclusion: In the present study, we found significant difference in biochemical markers between HCV patients and controls. In HCV patients, the biochemical markers were dependent on HCV genotypes, and their levels in genotype 1a were higher than genotype 3a. In conclusion, biochemical markers are one of the most important factors for the identification of treatment.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
