Comparison of the efficacy of using paclitaxel-eluting balloon and plain balloon angioplasty for arteriovenous fistula in hemodialysis patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v6i5.541Keywords:
Arteriovenous access, Hemodialysis, angioplasty, paclitaxel-eluting balloonAbstract
Introduction: Arteriovanous (AV) access failure is one of the main problems in patients with end stage renal disease (ESRD), who receive hemodialysis. Balloon angioplasty is a favorable method for managing vascular access failure. The purpose of this study was to compare the six-month efficacy of paclitaxel-eluting balloon and plain balloon angioplasty in failed AV access cases among hemodialysis patients.
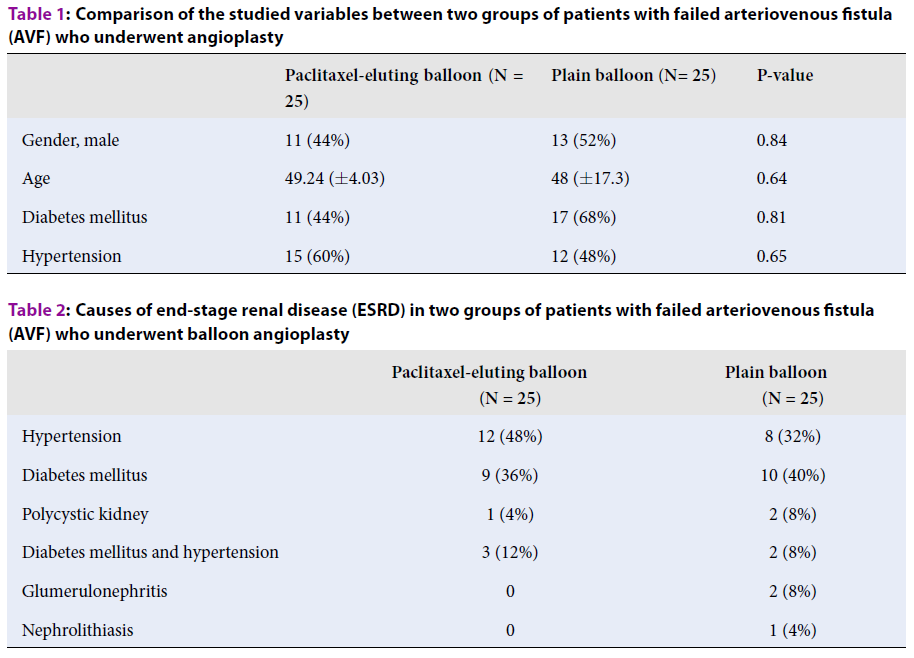
Methods: In this quasi-experimental study (http://en.irct.ir/trial/35333), 50 hemodialysis patients with failure of AV access (stenosis > 50%), who were candidates for angioplasty, were included. They were divided to receive either paclitaxel-eluting balloon (25 patients) or plain balloon (25 patients) angioplasty. Patients were followed up for six months with color Doppler ultrasonography and clinical examination for the hemodynamic success rate of angioplasty.
Results: After six months, 19 patients (76%) in paclitaxel-eluting balloon angioplasty group achieved hemodynamic success, which was significantly higher than plain balloon angioplasty group (13 patients, 52%) (P = 0.012). Age, gender, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and location of AVF (snuff box, forearm, and antecubital fossa) did not associate with hemodynamic success rate in any group.
Conclusion: The use of angioplasty with paclitaxel-eluting balloon was superior to plain balloon angioplasty for failed AV access cases in hemodialysis patients. It is recommended to use paclitaxeleluting balloon angioplasty in patients with failure of AV access and requirement for balloon angioplasty.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
