Prevention and treatment of brain damage in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats with Metformin, Nigella sativa, Zingiber officinale, and Punica granatum
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v6i7.554Keywords:
Diabetes mellitus, Brain damage, Ginger, Nigella sativa, Punica granatum, MetforminAbstract
Introduction: Diabetes mellitus (DM) is well-known metabolic disorder, which causes serious effects on human health with its complications. Many mechanisms has been postulated to cause DM related complications. One of the main complications is neuronal damage, for which no proper preventive and curative therapies are available.
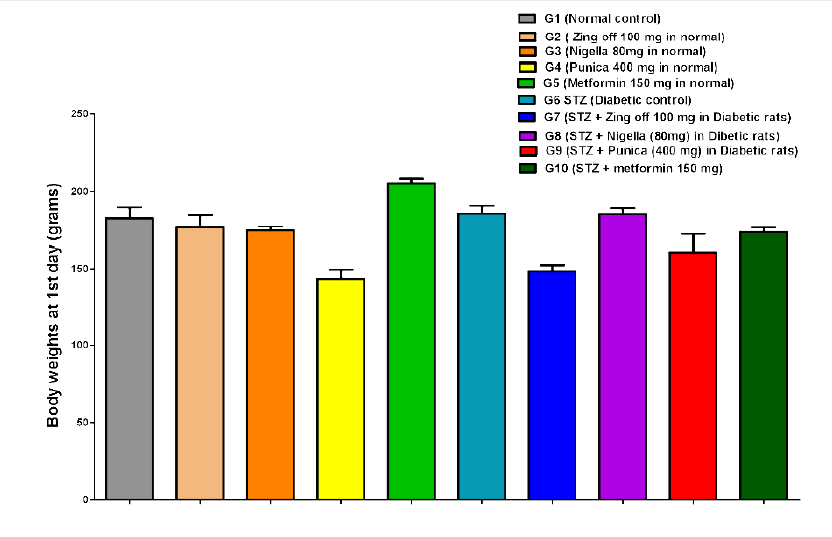
Methods: In this study the effects of Ginger, Nigella sativa, Punica granatum and Metformin were seen on the prevention and treatment of brain damage caused by diabetes mellitus in streptozotocin (STZ)- induced diabetes in rats. 50 adult Wistar albino male rats were used in the study, the rats were divided in 10 study groups. The body weight, serum glucose levels were measured, and histopathological examination was performed.
Results: In comparison to the diabetic control rats, significant increase in weight was found in animals of all the studied groups. Serum glucose levels reduced significantly in comparison to the STZ induced diabetic rats in all the animals. Histopathological examination showed prevention from brain damage and repair of the neuronal tissues by Ginger, Nigella sativa, Punica granatum and Metformin.
Conclusion: The studied substances were observed to possess preventive and curative effects on the brain damage caused by diabetes mellitus.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
