In vitro apoptosis induction ability of methanolic extract of Paramignya trimera root (Xao tam phan) in breast cancer stem cells
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v6i8.559Keywords:
Selective, anticancer, Paramignya trimera, Vietnamese breast cancer cell (VNBRCA1), apoptosisAbstract
Objective: Cancer has been considered as one of the world's leading causes of death. Recently, the Paramignya trimera plant, locally called ``Xao Tam Phan'', has become a popular Vietnamese medicinal herb that is used as alternative medicine for cancer treatment support with minimal side effects. In this study, we aimed to demonstrate the cytotoxicity of methanolic extract of Paramignya trimera on a Vietnamese breast cancer stem cell line (VNBRCA1) in vitro.
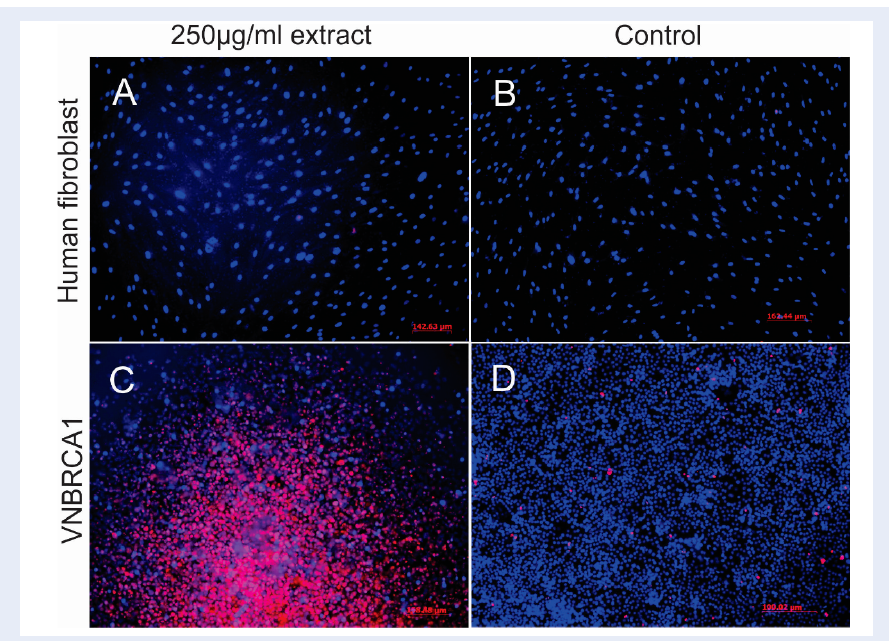
Methods: We used the MTT assay to determine the cytotoxicity of the extract on VNBRCA1 cells and human fibroblast (HF) cell line was used as a control for the plant extract treatment. Clinically used anticancer drug, doxorubicin, was used as a control drug (for relative comparison to the plant extract) to evaluate the selective cytotoxicity of the plant extract on VNBRCA1 and HF cells. We examined the apoptosis induction by the plant extract on VNBRCA1by Annexin V/7AAD staining and flow cytometry analysis. In addition, the morphology of apoptotic nuclei of treated cells was observed by fluorescent microscopy using double fluorescent staining: Hoechst 33342 and propidium iodide (PI).
Results: In comparison between the cytotoxicity of the plant extract and Doxorubicin on both cell lines (VBRCA1 and HF), we observed that plant extract was selectively cytotoxic against VNBRCA1 with an IC50 value of 10610 μg/mL, while Doxorubicin was discriminatorily cytotoxic against HF with an IC50 value of 0.135+/-0.09 μg/mL. We also found that the plant extract induced apoptosis VNBRCA1 in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, fluorescent microscopy revealed disintegrated nuclei of plant extract-treated cells, representing a hallmark of apoptosis.
Conclusions: These results showed that Paramignya trimera methanolic extract selectively killed VNBRCA1 cell lines, indicating that Paramignya trimera methanolic extract may represent a potential agent for cancer treatment.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
