Prevalence of blood pressure among students in Jiangsu Province, China
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v6i8.560Keywords:
Blood Pressure (BP), Jiangsu Province, Student, Body Mass Index (BMI)Abstract
Aim: Obesity and Blood Pressure (BP) is a serious public health issue. The study aims to assess the prevalence of BP and the factors associated with High Blood Pressure (HBP) among student in Jiangsu Province, China.
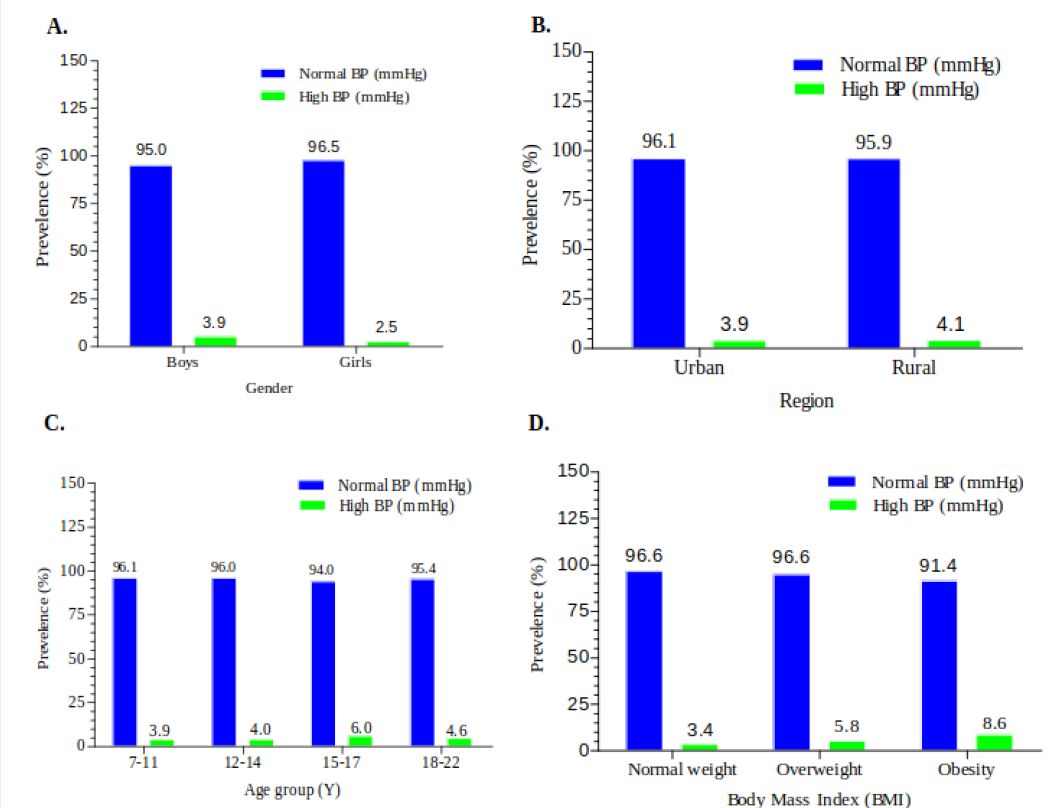
Methods: A cross-sectional epidemiological study. A total of 101886 students (62,065 boys and 39,821 girls) aged range from 7-22 yea rs were recruited in 2010-2013. Anthropometric measurements and BP prevalence were measured, and in addition, body mass index (BMI) was calculated. We assess the prevalence of BP according to the National Blood Pressure Reference for Chinese Han children and adolescents.
Results: A significant difference was observed in HBP prevalence in terms of student gender, region, age and BMI (P<0,001). Overweight and obesity were significantly associated with HBP (P<0.001).
Conclusions: The findings convey an important message to the parents, health institutions that urgent action is needed to enhance effective control of HBP among the overweight and obese, and among those are living in a rural area.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
