The effect of Phaseolus vulgaris pods extract on cytokines profile in the condition of alkali burn esophagus 2 degree
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v6i9.563Keywords:
chemical burns, cytokines, esophageal burn, inflammation, phaseolus vulgarisAbstract
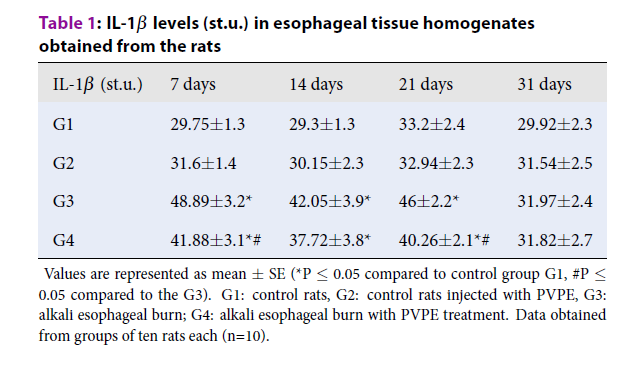
Introduction: As a result of alkaline substances entering the esophagus wall, necrosis occurs, as well as destruction of the mucous, submucosal and muscular layers of the esophagus. The cellular immune system plays an important role in regulating the various phases of the wound healing process, during which, depending on the time and through specific adhesion interactions, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, macrophages, and lymphocytes penetrate the site of the trauma and lead to an intensive proliferation of fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and keratinocytes. The substances of natural origins based on polyphenolic compounds are possible as a remedy for the normalization of physiological and biochemical parameters in a condition of various pathologies. Phaseolus vulgaris pods extract (PVPE) are an example of a rich source of bioactive compounds with proven human health benefits. Our results revealed imbalance of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in esophageal homogenates in rats with alkali burn of esophagus II degree, which can indicate a prolonged inflammation in the burned area. In the groups of animals with the alkaline burn of the esophagus, that were injected extract there can be traced a change of the indicators in the direction of normalization, indicating about the therapeutic effect of aqueous extract of pods of Phaseolus vulgaris.
Objective: The cellular immune system plays an important role in regulating the various phases of the wound healing process, and can be used as a marker of pathological post-burn wound healing, Phaseolus vulgaris pods extract (PVPE) are an example of a rich source of bioactive compounds with proven human health benefits. The aim of the study was to investigate changes in cytokines levels in rat esophageal supernatants in the condition of alkali burn esophagus second degree (AEB 2) and treatment with Phaseolus vulgaris pods extract.
Material and Methods: The animals were experimentally simulated with the alkali esophageal burn with 20% (grade II) solvent of NaOH. Levels of cytokines in esophageal tissue homogenates were done by ELISA.
Results: In the present study, we investigate the imbalance of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in esophageal homogenates in rats with AEB 2, which can indicate a prolonged inflammation in the burned area. In the groups of animals with the AEB 2, that were injected extract there can be traced a change of the indicators in the direction of normalization.
Conclusion: The administration of the extract, in conditions of alkaline burn of the esophagus, contributes change of the indicators in the direction of normalization indicating the therapeutic effect of aqueous extract of pods of Phaseolus vulgaris.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
