Deciphering the role of AMPK-related kinase 5 in human cancer progression and metastasis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v6i10.568Keywords:
ARK5, biomarker, cancer, epigenetics, invasion, tumor proliferationAbstract
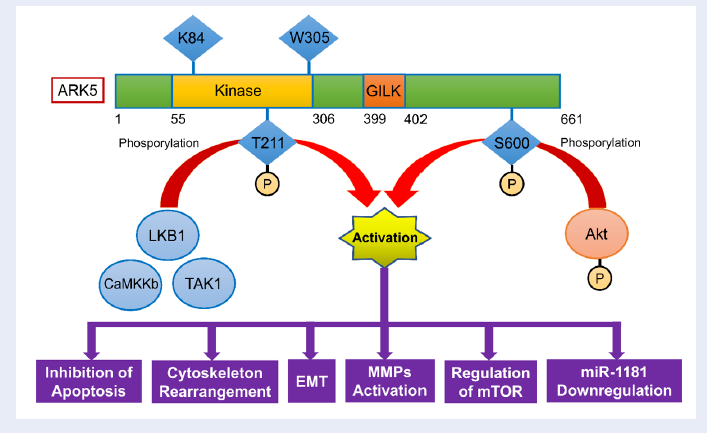
Malignancies related mortality is currently growing at an alarming rate. Early detection of cancer is vital in order to improve survival rates of cancer patients, and biomarker detection is regarded as one of the most promising approaches. Recent studies have reported that elevated AMPK-related kinase 5 (ARK5) expression is associated with tumor progression and metastasis in several human malignancies. Several pathways are also influenced by the presence of ARK5, most notably the PI3k-Akt pathway, m-TOR phosphorylation, and several pathways that induce increased tumor invasion activity. Additionally, ARK5 expression are linked to miR-1181 down-regulation, which promotes epithelial mesenchymal transformation in ovarian cancer cells. Furthermore, ARK5 gene transcription is also affected by the interaction of c-MAF and MAFB with both MARE core sequences present in the ARK5 promoter. Based on the current evidences, ARK5 might be the master regulator of cancer progression and metastasis, which could potentially serve as a novel target for cancer therapies.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
