Hibiscus sabdariffa extract as anti-aging supplement through its antioxidant and anti-obesity activities
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v7i1.584Keywords:
Hibiscus sabdariffa, pancreatic lipase, alpha-glucosidase, antioxidant, anti-obesityAbstract
Introduction: Imbalance between total energy intake and expenditure causes accumulation of excess fat and sugar in the body which leads to development of diabetes mellitus type II, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. These harmful diseases accelerate aging and cause fatal metabolic disorders as people age. Inhibition of pancreatic lipase, and alpha glucosidase digestive enzymes is a step that can reduce excess fat and sugar from the body, which is an essential component of healthy aging.
Methodology: In this study, aqueous and 50% ethanolic extracts of Hibiscus sabdariffa were investigated for their inhibitory activities on pancreatic lipase and alpha-glucosidase, in addition to their antioxidant activities (using UV-vis spectrophotometer).
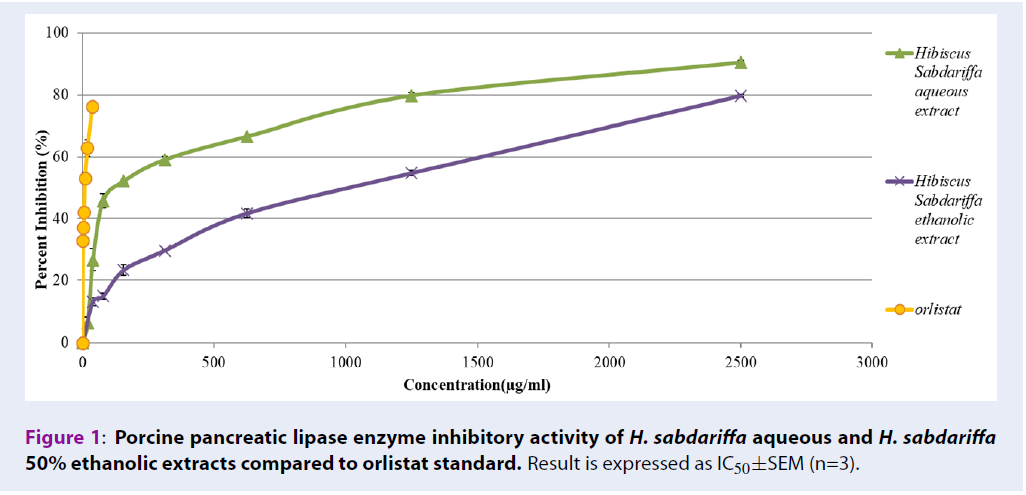
Results: Both extracts displayed antioxidant properties, indicated by IC50 of 5166.80 mg/mL for H. sabdariffa aqueous extract and 2809.10 mg/mL for H. sabdariffa 50% ethanolic extract. The extracts also suppressed the activities of pancreatic lipase and alpha-glucosidase enzymes, which suggests possible antiobesity and anti-diabetic activities. H. sabdariffa aqueous extract inhibited pancreatic lipase activity with IC50 of 167.5+/-12.7 mg/mL, whereas H. sabdariffa 50% ethanolic extract inhibited the enzyme with an IC50 of 790.65+/-16.02 mg/mL. Both H. sabdariffa aqueous and ethanolic extracts also successfully inhibited alpha-glucosidase enzyme activity with IC50 949.88 +/-10.83 mg/mL, and 378.33 +/-4.20 mg/mL, respectively.
Conclusion: Taken together, the outcome of the investigations offers the possibility of the extracts as an anti-obesity, anti-diabetic, anti-metabolic and anti-aging agent, which can be developed into supplements for adults to prevent the occurrence of these prevalent diseases and delay the onset and effects of aging.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
