Sodium citrate inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v7i3.592Keywords:
Liver cancer, Apoptosis, Citrate, HepG2, Nuclear fragmentationAbstract
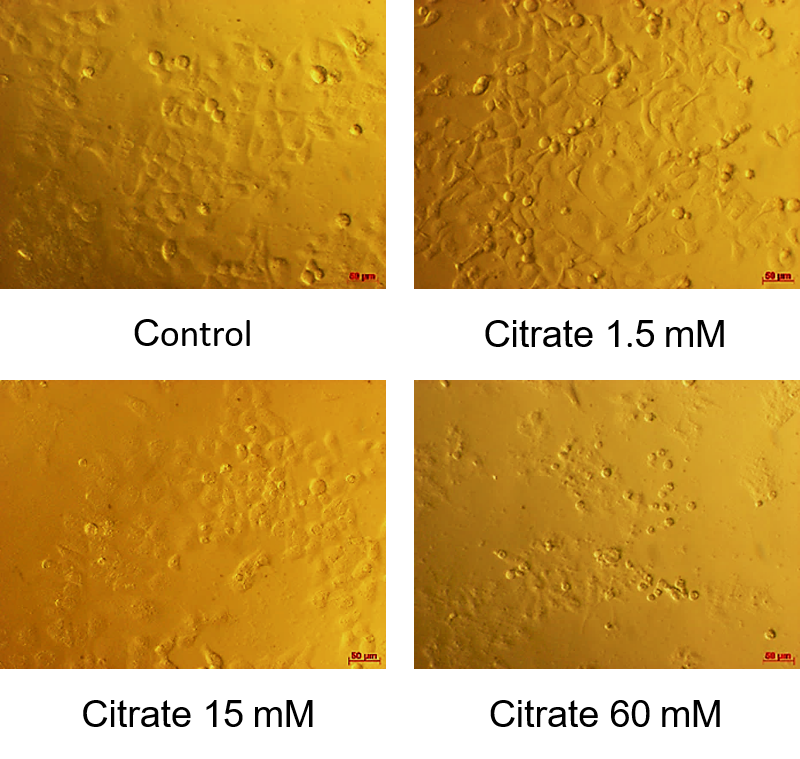
Introduction: Cancer cells rely on glycolysis to generate energy and synthesize biomass for cell growth and proliferation (the Warburg effect). Recent studies have shown that citrate has an inhibitory effect on several cancer cells, such as human gastric cancer and ovarian cancer, by inhibiting glycolysis. In this study, we investigated the effects of citrate on the proliferation and apoptosis induction of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Methods: HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cell line was used in this study. The cell proliferation was evaluated by Alamar blue assay. The apoptotic status of the HepG2 cells was recorded by Annexin V/7-AAD assay and caspase 3/7 activation assay. DNA fragmentation was evaluated by nucleus staining assay with Hoechst 33342.
Results: The results showed that citrate is able to inhibit the proliferation of HepG2 cells and induce apoptosis in these cells. The initiation time of apoptosis is 4 hours after treatment with 10 mM citrate. Morphology characteristics of DNA fragmentation and broken membranes were also recorded in the apoptotic cells.
Conclusion: In conclusion, our study demonstrates that citrate causes HepG2 cell death by the apoptosis pathway.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
