Investigating the histopathological effects of saffron petal (Crocus Sativus L.) hydroalcoholic extract on kidney and liver functional parameters in rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v7i4.600Keywords:
Saffron, Kidney, Liver, Histopathology, Wistar ratAbstract
Background: Saffron is one of the main food products in Iran, and its countless medicinal properties have been used widely in traditional medicine. Many studies conducted and reported in the literature have shown that plant-based medicines, such as chemical drugs, may also have unexpected side effects. Thus, the present study aimed to investigate the histopathological effects of the hydroalcoholic extract of the saffron petal (HAESP) on the liver and kidney, particularly on their functional parameters in rats.
Methods: The first group (control) received ordinary daily dietary regime. In addition, Groups 2, 3 and 4 were fed an ordinary dietary regimen along with HAESP (at 200, 400, or 600 mg/kg/day). The treatment was continued on a daily basis for four weeks, and upon the termination of the treatment, blood samples were collected from all the rats. Then, tissue samples were prepared from the animals’ kidney and liver for histological studies.
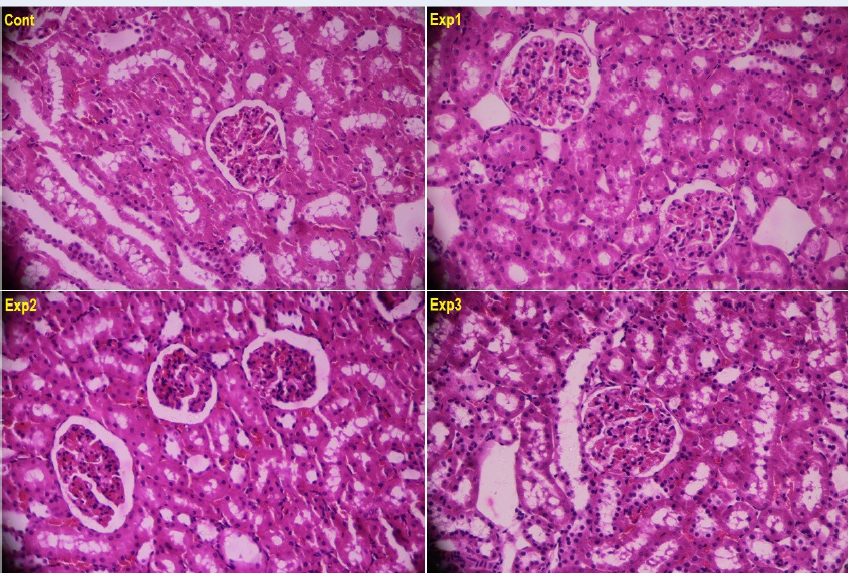
Results: The histological results are indicators of notable changes in the glomerulus, tubules, and interstitial tissue of the kidney cross-sections for the groups receiving HAESP. In the central vein region and the port space of the liver cross-sections, dose-dependent changes were found in the groups that had received HAESP. The study results also suggest a considerable statistical increase in the mean levels of renal enzymes and hepatic enzymes in different groups receiving HAESP.
Conclusion: The findings of the present study reflect the idea that the saffron petal hydroalcoholic extract can be effective even on renal and hepatic cells, and even in non-poisonous dosages. Therefore, care should be exercised in using the extract for its potentially therapeutic effects.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
