The predictive value of vascular endothelial growth factor-A gene polymorphism for clinical outcomes among acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients: A single center prospective study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v7i5.602Keywords:
ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, single nucleotide polymorphism G634C, vascular endothelial growth factor, prediction, outcomesAbstract
Background: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is an angiopoetic factor; its variability in circulating levels is mediated by expression of specific VEGF-A gene variants. The aim of this study was to investigate the predictive role of VEGF-A gene polymorphism in clinical outcomes of STelevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients.
Methods: For the study, 135 patients with acute STEMI and 30 healthy volunteers were enrolled. The G634C polymorphism in VEGF-A gene was performed by real-time polymerase chain reaction at baseline. The 6-month combined clinical endpoint was then determined. Design: The study was an open prospective single-center cohort study.
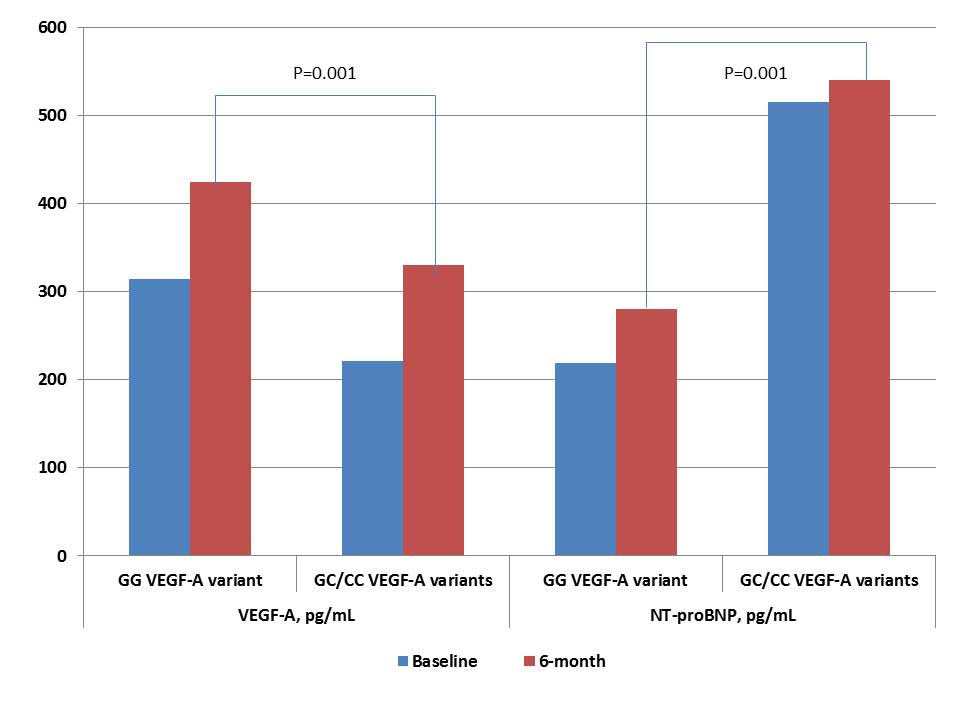
Results: The entire patient population was distributed into two groups based on the G634G-genotype (n = 70) and combination of G634C and C634C-genotypes (n = 65). Unadjusted multivariate regressive logistic analysis showed peak troponin I levels at admission, Killip class of heart failure > 2, GC/CC polymorphisms in VEGF-A gene, and dynamic increase of NT-pro brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) and VEGF-A levels for 6 months, which were independent predictors for the combined clinical endpoint. After adjustment for dynamic changes of NT-proBNP and VEGF-A levels, we found that GC/CC polymorphisms in the VEGF-A gene was an independent predictor of clinical outcome. Kaplan-Meier curves demonstrated that STEMI patients with GG VEGF-A genotype had a lower frequency of clinical combined endpoint accumulation when compared to those who had GC/CC VEGF-A genotypes (Log-rank p = 0.02).
Conclusion: The G634C polymorphism in the VEGF-A gene was found to be an independent predictor for 6-month clinical combined endpoint in STEMI patients.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
