Comparison of ultrasonography and X-ray test for lateral malleolar fracture in ankle sprain
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v7i8.624Keywords:
Ultrasonography, Lateral Malleolar Fractures, Emergency DepartmentAbstract
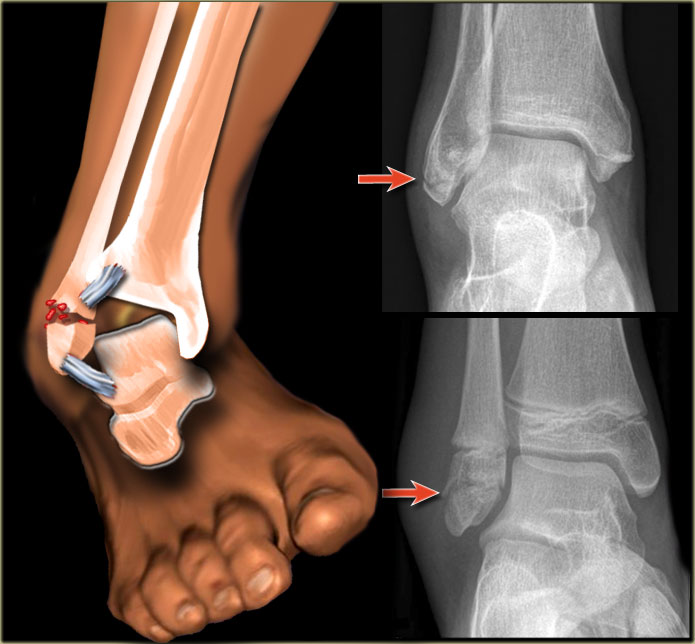
Introduction: The use of ultrasonography for diagnosing musculoskeletal injuries, especially fractures, in the emergency department is on the rise because of its good diagnostic value. This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic value of bedside ultrasonography in detecting the patients suffering from lateral malleolar fractures with an ankle sprain mechanism.
Methods: This prospective study was conducted on patients having acute ankle injuries with ankle sprain mechanism and diagnosed with lateral malleolar tenderness. All patients underwent bedside ultrasonography with a 7.5 - 10 MHz probe by an emergency medicine specialist who was assisted by a radiologist. Next, they underwent lateral ankle and anteroposterior (AP) X-rays by another emergency medicine specialist who was blinded from the ultrasonography results. The ultrasonography and X-Ray results were then compared.
Results: A total of 244 patients participated in this study, of whom 92 (37.70%) were diagnosed with lateral malleolar fracture through bedside ultrasonography and X-Ray tests. The results showed that ultrasonography had a sensitivity of 96.84% and a specificity of 97.31%. The positive likelihood ratio (PLR) and negative likelihood ratio (NLR) were 36.07 and 0.0325, respectively, and the positive and negative predictive values of bedside ultrasonography were 95.83% and 97.98%, respectively. Finally, the results indicated a percent agreement (accuracy) of 97.13% between the two tests with Kappa coefficient of 0.94 (z = 14.68, P value < 0.01).
Conclusion: The results of this study showed that bedside ultrasonography has a high sensitivity and specificity in the diagnosis of lateral malleolar fractures with an ankle sprain mechanism. Conducting further studies will lead to the use of this diagnostic test in the emergency department.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
