Toxicity effects of Cubic Cu2O nanoparticles on defecation rate and length in C. Elegans
This article was retracted on 19 February 2022 by author
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v7i10.639Keywords:
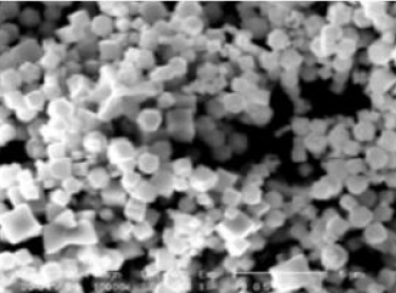
Neurodegeneration, C. elegans, Nanoparticles, Environmental Pollutants, Metal Oxide Catalyst, SEMAbstract
This article was retracted by author on 29 Feb 2022
Introduction: The increased presence of radiation and toxins in the atmosphere has given rise to fuel cells and nanoparticle technology with the ability to catalyze reactions at favorable energy levels. The purpose of this experiment was to determine the lasting effects of a synthesized catalyst on a model organism, Caenorhabditis (C.) elegans.
Methods: Copper sulfate was tested alongside copper(I) oxide (i.e. Cu2O) to dissociate the copper composition effects from those of the nanoparticles themselves. The prospect of testing both defecation rate and size differences allowed for C. elegans to be utilized due to their low maintenance costs, mapped neuronal pathways, and short-generation times.
Results: The results indicated significant toxicity effects in wild-type worms as witnessed by the decreases in nematode defecation rate and length by copper sulfate, with similar results in SMF-1 and PCS-1 mutants by Cu2O catalysts in cubic synthesized form.
Conclusion: These outcomes reinforce the known effects of metal oxides on pollutants and highlight the need for further testing with additional variables such as varying pH and temperature.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
