Green synthesized monodispersed silver nanoparticles’ characterization and their efficacy against cancer cells
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v8i8.686Keywords:
AFM, anticancer, biological preparation MTT assay, silver nanoparticlesAbstract
Background: In biomedical research, silver nanoparticles have attracted the attention of many scientists in drug delivery and other applications. This study investigates the characterization of biologically synthesized nanoparticles and their efficacy on cancer cells.
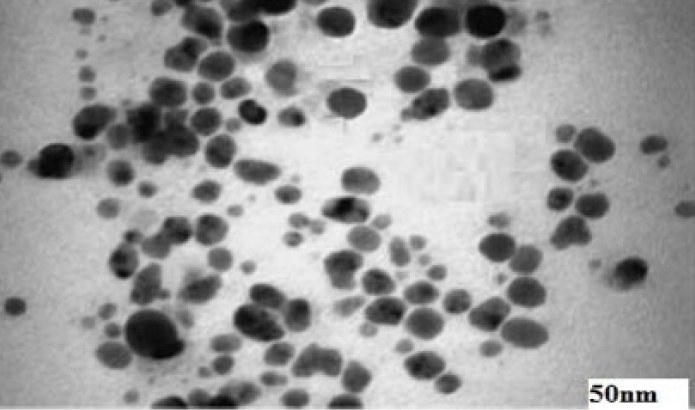
Methods: The characterization of biologically produced silver nanoparticles was accomplished using UV:visible absorption spectroscopy, which showed the maximum absorption at 422 nm. The structural morphology was carried out by transmission electron microscope (TEM) and atomic force microscope (AFM), and the anticancer efficacy of the biosynthesized compound was investigated on two cancer cell lines, namely HT-29 (colon cancer) and EAC.
Results: The morphological and structural examination revealed spherical, three-dimensional nanoparticles ranging between 5 to 50 nm. The results of the anticancer experiment, which was conducted using an MTT assay, revealed that the prepared silver had excellent anti-cancer activity against both tested cells, that is EAC cancer and HT-29 (colon cancer) cell lines.
Conclusion: This study confirms that silver nanoparticles can be biologically synthesized using Rhizopus stolonifer and used as anticancer substances in cancer therapy and drug delivery.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
