Recent Advances in the Role of Microorganisms in Cancer Incidence: Mechanisms and Health Precautions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v8i9.691Keywords:
cancer, carcinogenesis, incidence, health precaution, microorganismsAbstract
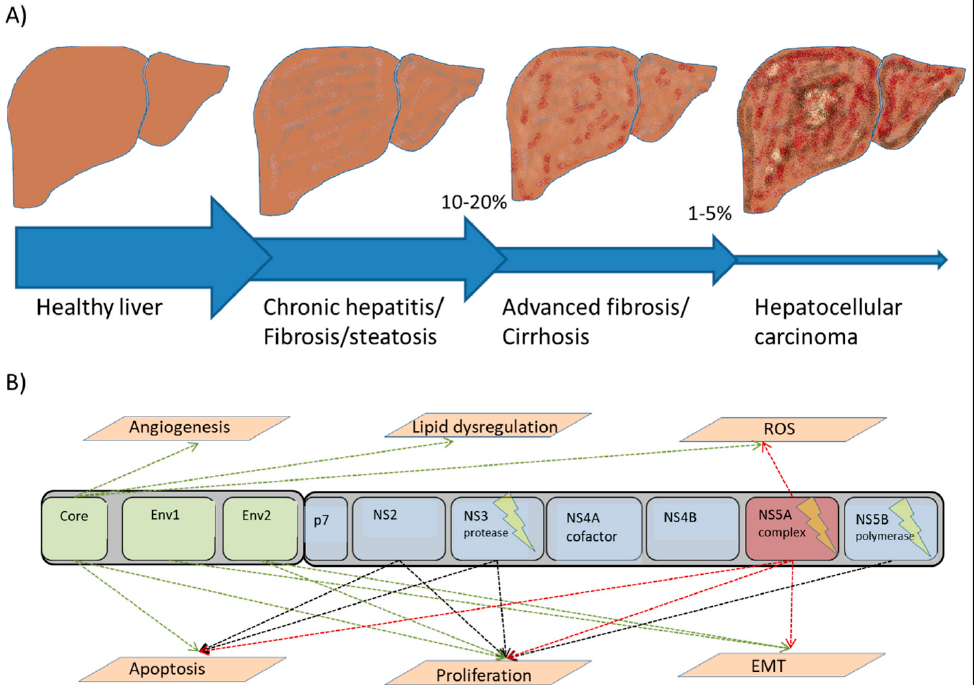
Humans harbor various microorganisms, some of which reside naturally in the body, and some of which are transferred from elsewhere. Many of these microbes are considered to be normal flora that do not cause disease, provided that they occur only in their normal anatomical site in the body. The development of malignant lesions requires a long incubation time, even after direct exposure to known carcinogens. Multistep tumorigenesis is required to transform a normal cell into a cancerous one. The role of different microbes in tumorigenesis has expanded to include their potential capacity to form and modulate several cancer hallmarks, including the alteration of the immune response, tumor-promoting inflammation, angiogenesis, tumor growth and proliferation, and pro-carcinogenic metabolite production. Furthermore, microbes may damage the host DNA and induce genomic instability. This review provides a basic overview of the process of tumorigenesis and the role of different microorganisms in cancer accuracy. Then this study discusses the different mechanisms of tumor induction by viruses, bacteria, protozoa, and fungi. Finally, it highlights the necessary health precautions that need to be taken to prevent the development of cancers.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
