Profile of Platelet Parameters in Coronavirus Disease – Positive Cases — An Observational Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v8i10.700Keywords:
COVID-19, platelet lymphocyte ratio, platelet neutrophil ratio, platelet parametersAbstract
Background: Coronavirus disease affects mainly the respiratory system. Other systems, including blood, are also affected. Blood cell abnormalities have varied between studies. The majority of patients present with platelet abnormalities.
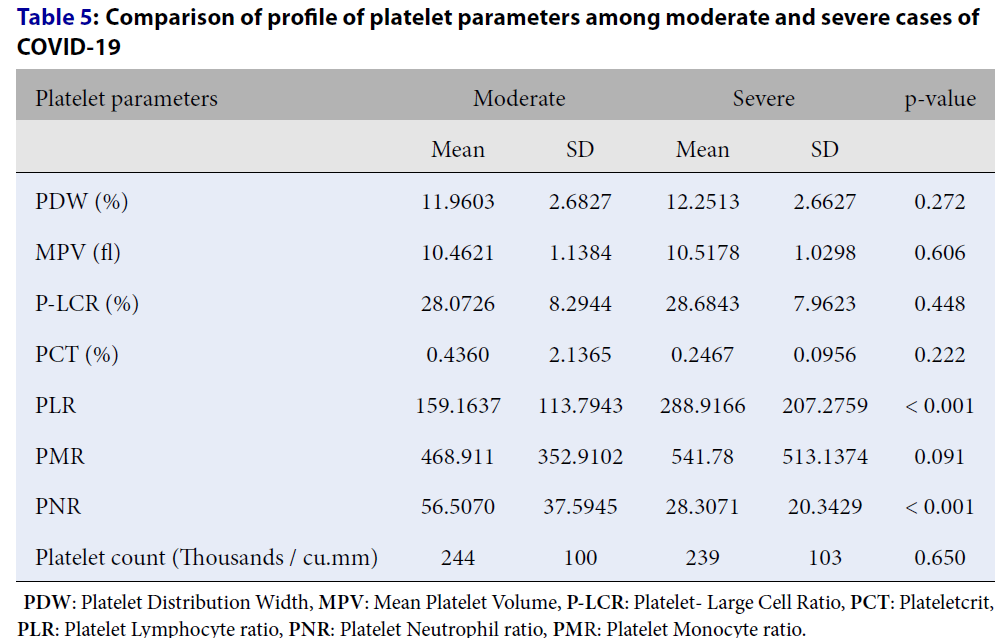
Methods: This was a laboratory observation study. All cases positive for the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) by reverse transcriptase — polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test during the study period were considered for inclusion. Platelet index data were captured from an automated hematology analyzer: platelet count, mean platelet volume (MPV), platelet distribution width (PDW), plateletcrit (PCT), and platelet–large cell ratio (P-LCR). Platelet lymphocyte ratio (PLR), platelet neutrophil ratio (PNR), and platelet monocyte ratio (PMR) were calculated. The cases were classified into two groups: moderate and severe. The difference in alteration of platelet parameters between moderate and severe COVID-19 cases was analyzed using SPSS 22 version software. A p-value of < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results: Most cases (44.9%) were in the age group of 41 – 60 years. The male-to-female ratio was 1.9:1. Moderate cases comprised 53.4%, and 46.6% of cases were severe. The association of PLR and PNR between moderate and severe cases was statistically significant. PLR was higher in severe cases than moderate cases, whereas PNR was higher in moderate cases than severe cases.
Conclusions: Studying platelet index profiles in COVID-19 patients can improve our limited knowledge of the disease progression regarding platelet parameters. PLR and PNR are the more reliable platelet parameters in managing COVID-19 patients, which help predict the prognosis and aid in improving therapeutic options for severe cases.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
