Impact of COVID-19 on Pregnancy and Maternal Health: An Update
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v8i10.701Keywords:
COVID 19, health care, infection, maternal, pandemic, pregnancy, vertical transmissionAbstract
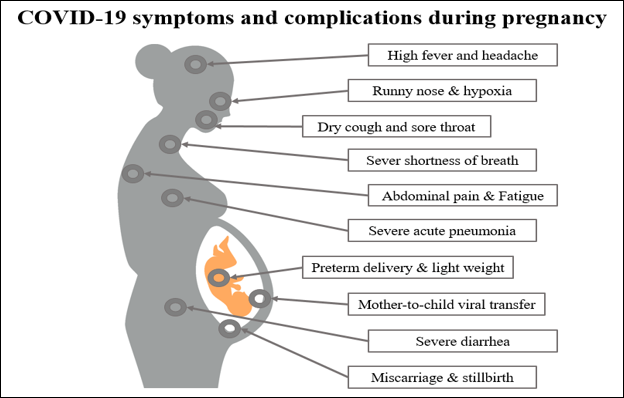
The current pandemic caused by the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is spreading at an accelerated rate globally. Global concerns were raised following its discovery in December 2019, as previous similar diseases. Diseases such as the severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and the Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (MERS-CoV) are known to lead to adverse outcomes in pregnant women and those in early maternal stages, with significantly higher rates of complication and mortality compared to other groups of individuals. The anatomical, physiological, and immunological changes that occur during pregnancy lead to higher risks associated with respiratory infections for pregnant women, as they can directly affect the well-being of pregnant women and infants. Vertical transmission of COVID-19 from mother to child was a concern, as such transmission could endanger a child. Three mechanisms of vertical transmission have been suggested: intrauterine transmission, placental blood transmission, and intrapartum transmission. This review discusses the impact and pathogenicity of COVID-19 on the well-being of pregnant and early maternal women, both the clinical aspect, health aspects, and diagnostic and therapeutic options. It will also discuss the adverse outcomes among pregnant women and newborn infants who contract the disease and the different mechanisms of vertical transmission from infected mother to child. The diagnostic and therapeutic approaches of COVID- 19 that have been recently used have also been highlighted, in addition to the challenges faced by pregnant women who have contracted the virus during the pandemic.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
