Identification of a novel de novo deletion mutation of desmin in a neonate with desminopathy
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v8i12.717Keywords:
cardiomyopathy, cardiovascular, desmin, desminopathy, mutation, whole-exome sequencingAbstract
Introduction: Whole-exome sequencing (WES), a high-throughput DNA sequencing method, has swiftly gained traction as a scalable approach for detecting novel de novo mutations and generating molecular diagnoses for genetic illnesses.
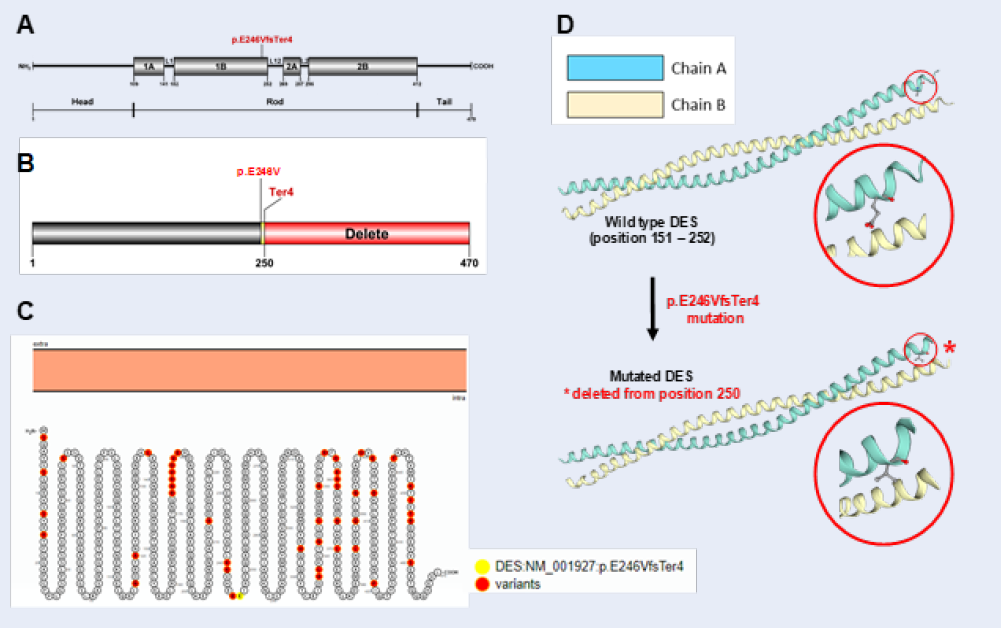
Case presentation: We describe a neonate girl with a novel de novo desmin (DES) variant. The patient was referred to our Department of Cardiology right after birth for multiple clinical cardiac and pulmonary presentations. Her family history was negative for cardiovascular diseases while her echocardiographic diagnosis indicated macrocardia, arrhythmia, ventricular septal defect (VSD) in association with tricuspid regurgitation. Electrocardiography showed prolonged QTc interval, premature atrial contractions following pulmonary arterial hypertension. The patient had a surgical VSD closure at the age of seven months. The healthy infant was fit enough to be discharged six weeks later. Whole-exome sequencing identified a novel de novo heterozygous frameshift deletion mutation p.E246VfsTer4 in DES gene. Among the variants detected, mutation in DES was predicted to be the only pathogenic one, causing desminopathy phenotype for the patient.
Conclusion: This report strengthens the genetic aetiology for desminopathy and highlights the need for screening an intriguing candidate, those who have the DES gene in congenital cardiovascular probands.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
