Long QT syndrome: Identification of a novel de novo mutation of calmodulin in a newborn girl
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v9i1.719Keywords:
Calmodulin, Cardiovascular, Long QT syndrome, Mutation, Whole exome sequencingAbstract
Background: Long QT syndrome (LQTS) is a genetically and phenotypically heterogeneous disorder of ventricular myocardial repolarization that is typically characterized by prolongation of the heart rate-corrected QT interval on a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG). LQTS has a complicated etiology since great genotypic and phenotypic overlapping among LQTSs limits the establishment of a diagnosis based solely on clinical features.
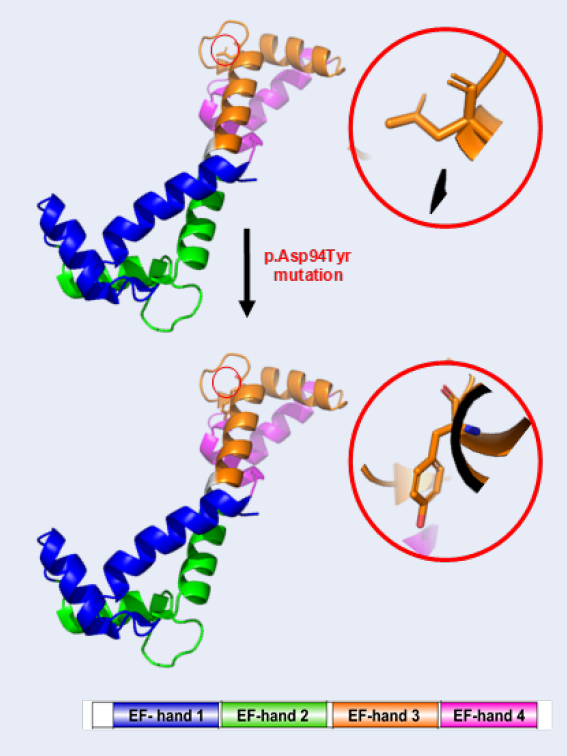
Case presentation: Here, we describe a Vietnamese newborn with a novel calmodulin (CALM2) variant. The patient was referred to the Department of Cardiology at Children's Hospital 2 in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam for multiple clinical cardiac presentations. The patient's family history was negative for cardiovascular diseases; however, she suffered from recurrent syncope and QT interval prolongation on resting in a 12-lead surface ECG. A fetal echocardiogram at 29 weeks detected signs of congenital heart disease. The newborn patient then suffered from sudden cardiac arrest and required cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Two weeks later, the patient suffered from torsade de pointes for the third time and required electrical shocks. An endotracheal tube was placed through the mouth into the trachea to facilitate breathing. Unfortunately, the patient expired at 3 months of age due to serious inflammatory issues. Whole exome sequencing (WES) — a technique used to determine variations in all coding regions (exons) of the known genes — validated a total of four rare variants in four cardiomyopathy (CM) genes, the CALM2, DSP, MYBPC3, and SPEG genes. We identified a novel de novo heterozygous missense mutation, c.280G > T (p.Asp94Tyr), in the CALM2 gene (NM_001305626) encoding calmodulin, which is a ubiquitous calcium-binding protein that is important for a myriad of intracellular signaling events of cardiac function.
Conclusion: The results obtained in this study support the ``pan-cardiomyopathy panel'' approach, in which the molecular diagnosis of LQTS, the early identification of arrhythmia development, and the improved clinical management of cardiovascular disease patients are applied.
Trial registration: The procedures were reviewed and approved by the Ethical Committee of the University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, under the number UMP-VN 2018-10a12.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
