Onion Peel Quercetin Attenuates Ethanol-Induced Liver Injury in Mice by Preventing Oxidative Stress and Steatosis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v9i6.745Keywords:
Attenuates, fibrosis, hepatocytes, lymphocytes, silymarin, steatosisAbstract
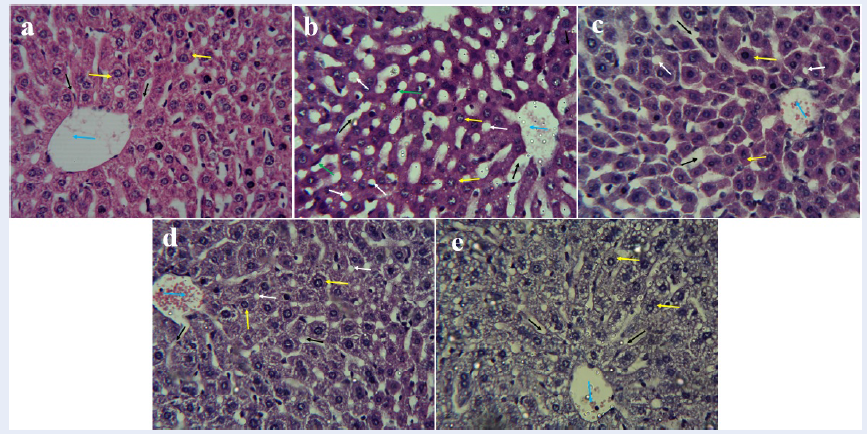
Introduction: Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is a histological abnormality of the liver that ranges from steatosis to fibrosis/cirrhosis. This study examines the role of onion peel quercetin (OPQ) on oxidative stress, liver function and steatosis in ethanol-treated mice over two phases, protective and therapeutic.
Methods: In each phase, 25 mice were divided equally among five groups (n = 5). In both phases, groups 1 and 2 received vehicle and ethanol, respectively, for 8 days. In the protective phase, groups 3 - 5 received 50 mg/kg OPQ, 100 mg/kg OPQ and 100 mg/kg silymarin, followed by ethanol for 8 days. Mice in these groups were euthanized on day 9. In the therapeutic phase, groups 3 - 5 received ethanol for 8 days and were then treated with 50 mg/kg OPQ, 100 mg/kg OPQ and 100 mg/kg silymarin for an additional 8 days before being euthanized on day 17.
Results: Significant decreases in ALT, AST, and ALP serum levels were observed in mice that received OPQ and silymarin compared to mice that received ethanol (P < 0.05). The catalase activity of mice treated with 50 mg/kg OPQ was significantly higher than in controls (P < 0.05). OPQ treatment significantly improved MDA levels relative to controls (P < 0.05). Hepatocyte degeneration, steatosis, and increased lipid peroxidation were observed in ethanol-treated mice. OPQ significantly decreased ALP, ALT, and AST serum levels compared with ethanol treatment (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Therefore, OPQ can be used as an antioxidant to delay the onset and progression of liver disease by preventing lipid peroxidation, regulating liver function, and promoting albumin synthesis.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
