Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a promising biomarker for the diagnosis of psoriasis in Pakistan
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v9i9.768Keywords:
Biomarker, Hematology, neutrophils to lymphocyte ratio, Pakistan, PsoriasisAbstract
Background: Psoriasis is a skin inflammation characterized by papules and plaques on the skin surface. Almost 125 million people are affected by psoriasis worldwide. This study aimed to evaluate whether the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) can be used as a biomarker for the diagnosis of psoriasis.
Methods: Blood samples of patients with psoriasis and healthy controls were collected for complete blood count testing. A t-test was applied to estimate the difference in the hematological parameters between the two groups.
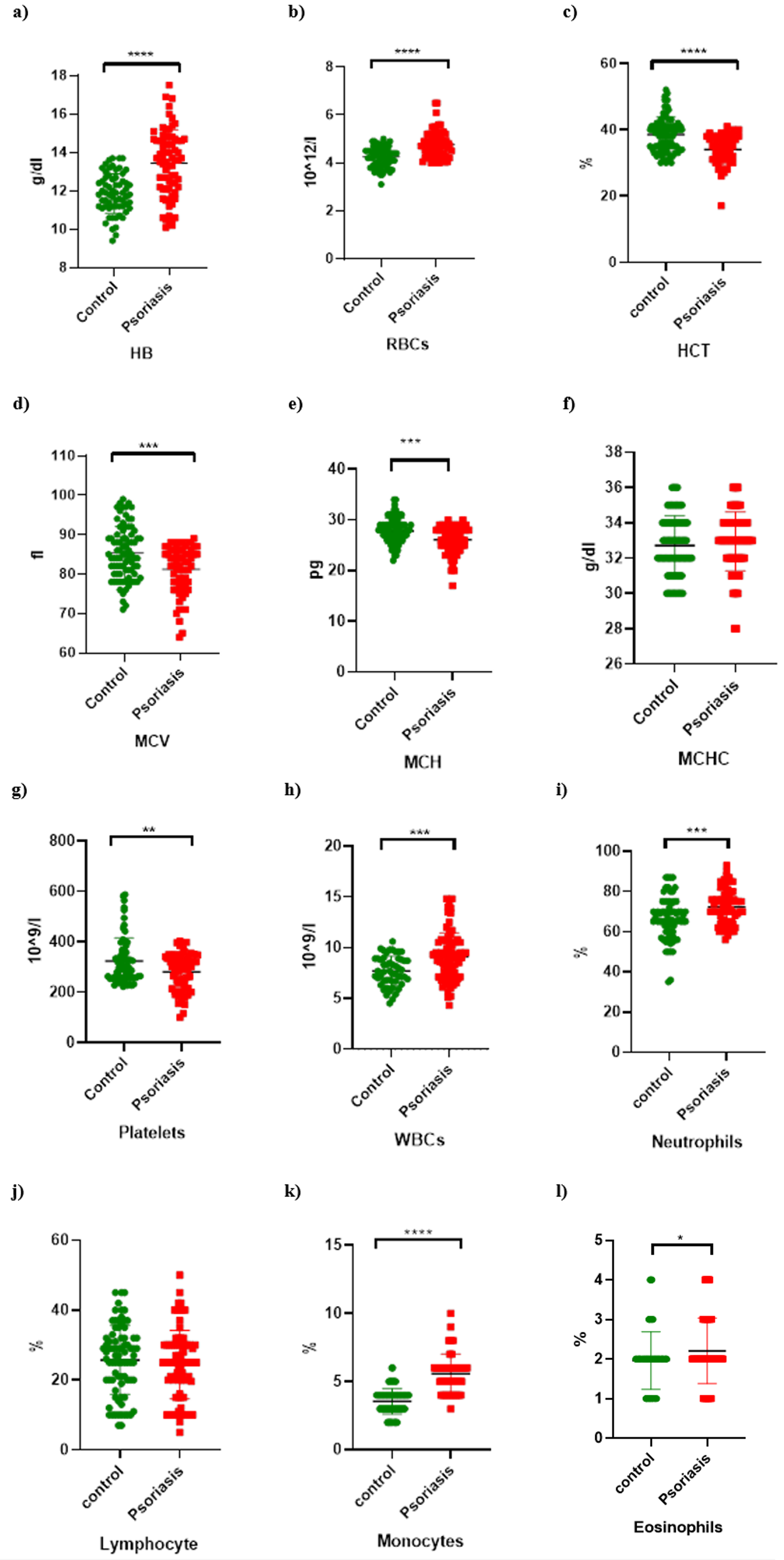
Results: The hemoglobin level (p < 0.0001), hematocrit level (p < 0.0001), red blood cell count (p < 0.0001), mean corpuscular volume (p = 0.0002), platelet count (p = 0.0039), white blood cell count (p = 0.0002), neutrophil count (p = 0.0001), monocyte count (p < 0.0001), and eosinophil count (p = 0.0467) significantly differed between the groups. Meanwhile, the mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (p = 0.3989) and lymphocyte count (p = 0.3842) did not. The patients with psoriasis had a higher neutrophil count and a lower lymphocyte count than the healthy controls. The NLR was significantly elevated in the patients with psoriasis.
Conclusion: The NLR is a potential biomarker for the diagnosis of psoriasis.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
