Overview of the advantages and disadvantages of chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy in the tumor microenvironment
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v9i10.772Keywords:
Cancer-associated stromal cells, T-cell therapy, Toxicity, Transforming growth factor, Tumor microenvironmentAbstract
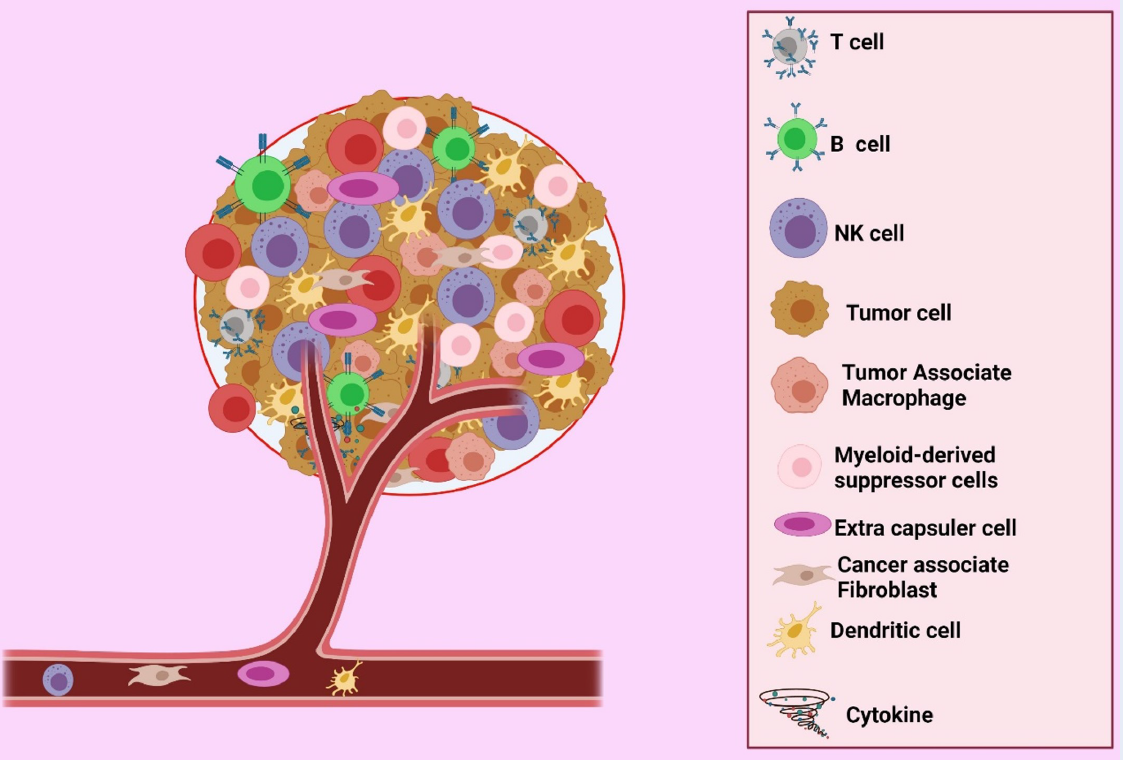
T cells genetically modified to express a receptor that identifies a specific antigen, known as chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, have led to advancements in the treatment of hematological malignancies and the tumor microenvironment. CAR-T cells target the origin of tumors on the vascular side of inflammatory cytokines where the tumor microenvironment forms and block immunosuppressive checkpoints. The efficacy of CAR-T cell treatment remains controversial because its toxicity damages organ structures, including neurological, pulmonary, cardiac, and muscular structures, and causes fatal abnormality. In this review, we discuss the advantages and disadvantages of CAR-T cell immunotherapy in the tumor microenvironment.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
