Cytoprotective effect of alpha-2-macroglobulin against pesticide-induced generation of ROS in neuronal SH-SY5Y cells
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v10i2.792Abstract
Introduction: Many clinical studies have demonstrated that continuous exposure to pesticides, especially organophosphates and pyrethroids, causes toxicities such as carcinogenicity and neurotoxicity that lead to disorders such as diabetes, lung cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases. The mechanism underlying pesticide-induced neurotoxicity involves the production of ROS, which causes neuronal injury through oxidative stress.
Methods: In the present study, the neuronal SHSY5Y cell line was used to investigate the effect of the pesticides chlorpyrifos (organophosphate), aldicarb (carbamate), and deltamethrin (pyrethroid) on ROS-mediated toxicity and the protective effect of alpha-2-macroglobulin (a2M), a protease inhibitor and beta-amyloid plaque scavenger in the human brain. For cell viability and cytotoxicity, the MTT assay was performed. To monitor ROS production, assays such as DCFHDA, H2O2, and MDA were performed, along with assays of the activity of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase.
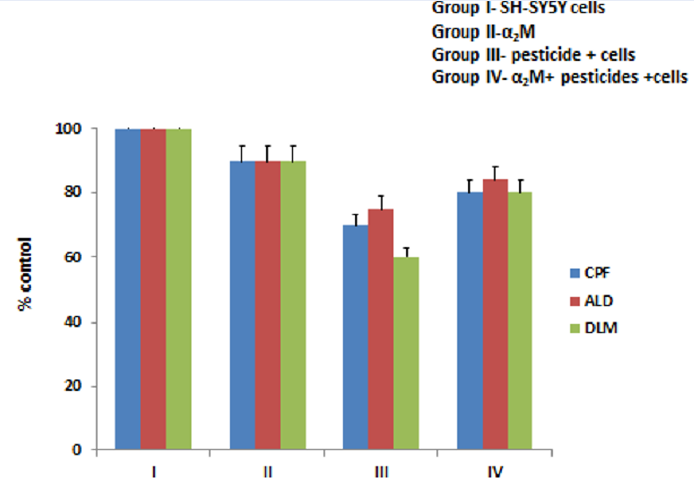
Results: The experimental findings suggest a cytoprotective role for a2M in ROS-mediated toxicity that causes neuronal injury in humans.
Conclusion: Hence, a2M could be possibly used as a protective agent against oxidative neurotoxicity caused by pesticides.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
