Interleukin-17A enhances osteogenic differentiation by activating ERK/MAPK in stem cells derived from human exfoliated deciduous teeth
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v10i5.810Keywords:
Osteogenic differentiation, ERK/MAPK signalling pathway, stem cell, interleukin-17AAbstract
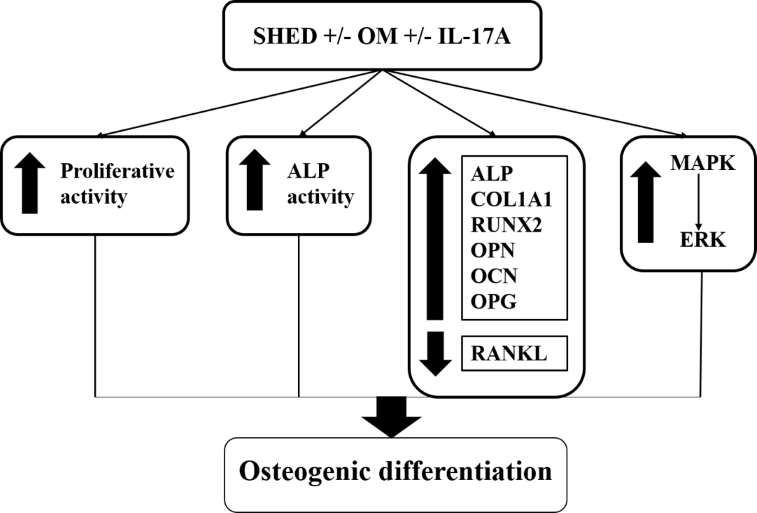
Introduction: Human exfoliated deciduous teeth?derived stem cells (SHEDs) have been shown as an excellent source of bone regeneration. Interleukin-17A (IL-17A) facilitates bone differentiation in various cell types, including SHEDs. In this study, we have demonstrated IL-17A?s stimulating effect on SHEDs in osteogenic differentiation and further evaluated the role of the ERK/MAPK signaling pathway in this process.
Methods: The function of IL-17A in osteogenic differentiation, proliferative activity, and MAPK cascade activation in SHEDs were investigated.
Results: IL-17A significantly enhanced proliferative and alkaline phosphatase activities in SHEDs. Furthermore, the expression levels of different osteogenic proteins including COL1A1, ALP, OPN, RUNX, and OCN were significantly elevated in IL-17A-treated SHEDs. Moreover, IL-17A triggered MAPK signaling in SHEDs, as evidenced by significant upregulation of both downstream ERK targets, P38 and JNK pathways, and upstream activators. In addition, ERK/MAPK activation time-dependently established the participation of MAPK signaling in SHED osteogenic differentiation.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that IL-17A-induced ERK/MAPK signaling pathway activation is necessary for SHEDs to differentiate into osteoblasts. This reiterates the significance of this particular intracellular signaling pathway in controlling SHED osteogenic differentiation, which is a promising source of bone tissue regeneration.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
