Structural genomics and immunoinformatics analyses of non-structural protein 6 (NSP6) and its probable role in autophagy
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v10i7.818Keywords:
COVID-19, NSP6, Variation, Autophagy, MutationAbstract
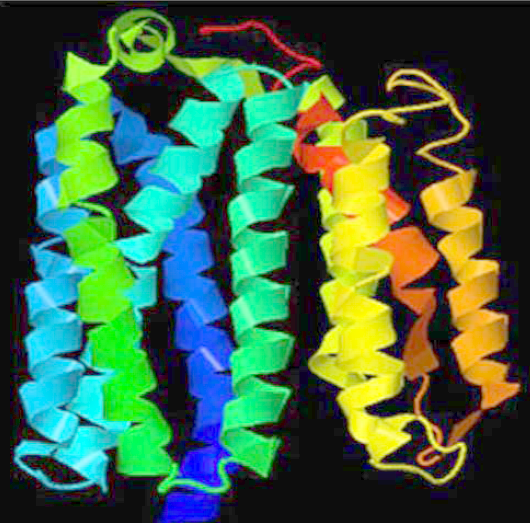
Autophagy is a natural cellular mechanism in which cellular components such as long-lived proteins and damaged organelles are degraded in response to starvation by forming autophagosomes. Viruses activate the autophagy process, which generates innate immune protection in the host against infection. While the actual molecular mechanism of this contagious viral infection remains unknown, studies on some other betacoronavirus show that their infection of host cells inhibits the autophagy process, resulting in autophagosome accumulation inside the cells. Non-structural protein 6 (NSP6) is crucial in blocking autophagosomes/autolysosome vesicle formation, which are more numerous and smaller than autophagosomes formed upon starvation. Because of its vital role in autophagy, NSP6 can be used as an effective drug target to combat severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infections. Therefore, this study aims to detect the mutations in the NSP6 of Indian isolates compared to Wuhan-type isolates. The NSP6 protein of Indiantype SARS-CoV-2 isolates contained 654 point mutations. Furthermore, secondary structure, energy change upon mutation, physicochemical properties, and hydropathy index of wild and mutated proteins were compared, clearly showing that mutations altered NSP6 stability. An immunoinformatics approach was also attempted to identify the B-cell and interferon (IFN)-inducing epitopes for using NSP6 as a probable vaccine candidate. Therefore, this study explored an important drug target (NSP6) essential for autophagy and assembly of coronavirus replicase proteins.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
