Assessment of circulating miRNA-218, miRNA-222, and miRNA-146 as biomarkers of polycystic ovary syndrome in epileptic patients receiving valproic acid
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v10i9.833Keywords:
Anti-seizure medication, Sexual disorders, miRNA-146, miRNA-222, miRNA-218Abstract
Introduction: This study was designed to evaluate the relationship between taking sodium valproate (VPA) and the onset of polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) in women with epilepsy (WWE) and analyze the biochemical factors and expression levels of three miRNAs as diagnostic or predictive biomarkers. These miRNAs target numerous genes and molecular pathways involved in hyperandrogenism, insulin resistance, and obesity in PCOS patients.
Methods: The study was conducted on 120 WWE aged 18?35 years before and after monotherapy with VPA and 120 women with PCOS (WWP). After collecting the plasma samples of patients, the total RNA was extracted. Then, the miRNA-218, miRNA-222, and miRNA-146 expression levels were determined via qRT? PCR.
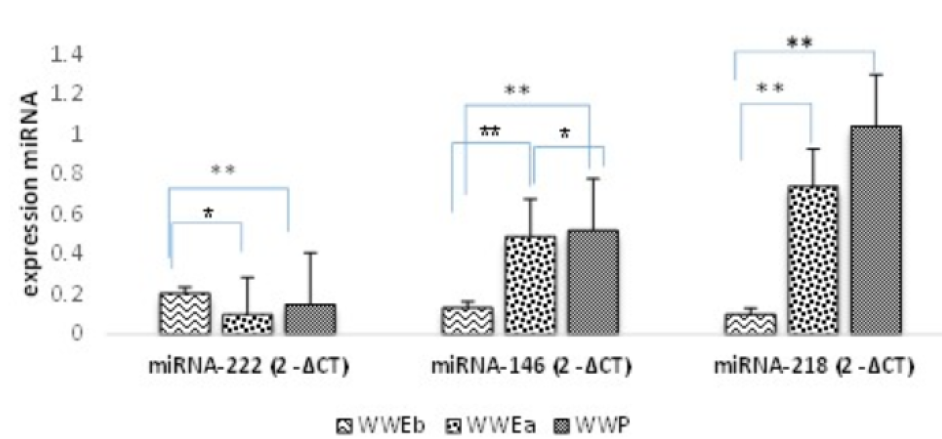
Results: In this study, the relative expression levels of miRNA-146 and miRNA-218 showed a significant increase in the WWP and treated epileptic patients (P < 0.01). However, the expression level of miRNA-222 significantly (P0.05) reduced. Our finding showed a significant increase in the concentrations of anti-M?llerian hormone (AMH), free testosterone, and estradiol and an increased LH/FSH ratio after treatment compared with pre-treatment with VPA (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Significant changes were observed in the expression of the examined miRNAs after receiving VPA, especially miRNA-218. In addition, a significant correlation was found between PCOS and AMH, free testosterone, estradiol, and the LH/FSH ratio. Therefore, the miRNA-218 expression and these biochemical factors are valuable biomarkers for predicting PCOS symptoms. They are cost-effective for controlling side effect and timely medication adjustments in patients receiving VPA.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
