PARP inhibitors in newly diagnosed or recurrent ovarian cancer maintenance therapy: evidence of efficacy and safety from randomized controlled trials
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v10i12.851Keywords:
Ovarian cancer, Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors, PARP inhibitors, clinical trial, Systematic reviewAbstract
Objective: This review aimed to systematically synthesize and report the clinical outcomes of poly-ADP ribose polymerase inhibitors (PARPis) for maintenance therapy among ovarian cancer (OC) patients.
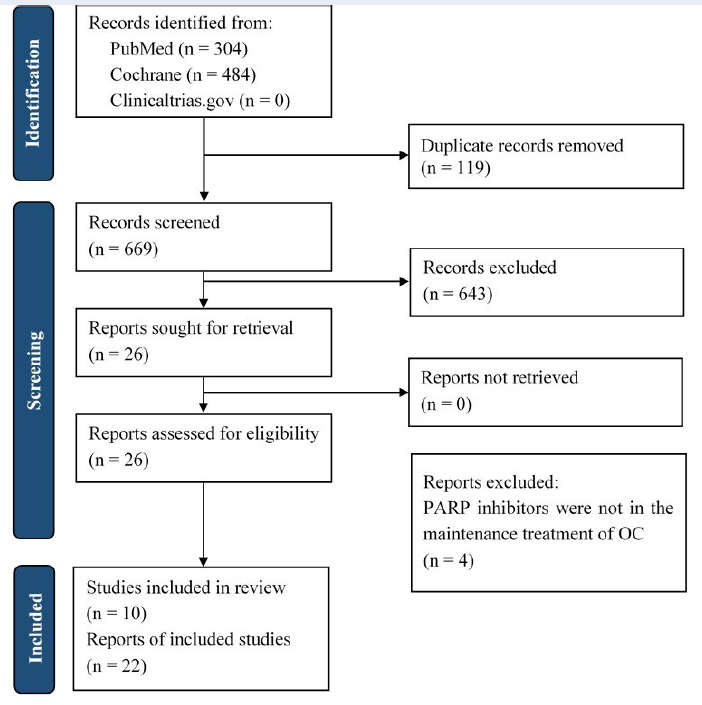
Methods: This review was based on the updated PRISMA statement 2020. Eligible studies were identified from PubMed and the Cochrane Library from the database inception to October 7, 2021. Randomized controlled trials reporting the clinical outcomes of PARPis as maintenance therapy for OC were included in this review. The Risk of Bias 2 tool was used for the quality assessment of studies.
Results: Out of 26 studies, 10 were eligible. For patients with newly diagnosed disease, compared with placebo, either olaparib or niraparib considerably prolonged progression-free survival (PFS), with hazard ratios (HRs) of 0.59 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.49–0.72) and 0.62 (95% CI: 0.50–0.76), respectively. Among recurrent patients, olaparib, niraparib, and rucaparib also achieved higher PFS than placebo, with HRs of 0.39 (95% CI: 0.27–0.55), 0.32 (95% CI: 0.23–0.45), and 0.35 (95% CI: 0.28–0.45), respectively. Regarding adverse events, patients taking PARPis experienced a higher risk of hematologic events than the placebo group.
Conclusions: PARPis as maintenance therapy were beneficial in PFS improvement for OC patients. However, the considerable risk of hematologic events must be considered when using this treatment class.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
