Computational and expression analysis of microRNA-149-5p and its target, interleukin-6, in chronic kidney disease
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v10i12.852Keywords:
Chronic kidney disease, Interleukin -6, microRNA-149-5p, gene expression, treatmentAbstract
Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is an ailment marked by a reduction in the glomerular filtration rate or the presence of proteinuria. Millions of people are affected worldwide, and so far, the mechanisms underlying these effects remain mostly unknown. Recently, the role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in several cellular processes associated with the development of diseases has been discovered. Studies have suggested that miR-149-5p may play a role in renal function and kidney disorders and be linked with inflammation, fibrosis, or apoptosis within the kidneys. In addition, miR-149-5p often targets signaling pathways, including TGF-β, Wnt/β-catenin, and NF κB. Hence, this study focused on miR-149-5p and its biomarker, interleukin-6 (IL-6), as potential indicators of CK D. Computational analyses were employed for miR-149-5p identification within CKD genome sequences, revealing its potential involvement in disease processes.
Methods: In this study, a total of 20 patient and normal blood samples were collected and stored for analysis. To detect miR-149-5p in CKD, target scanning, miRbase, and the National Centre for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database were used, whereas RNA fold, melt curve, and Ct were utilized to construct the secondary structure and analyze miR-149-5p levels. A similar investigation was conducted to determine the IL-6 gene’s expression levels.
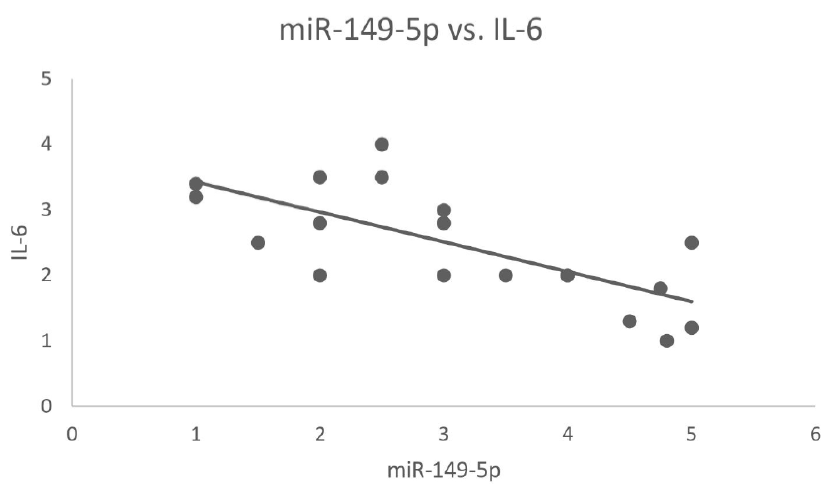
Results: Upon thoroughly studying the secondary structure, hsa-miR-149-5p’s lowest free energy was found to be −52.70 kCal. Additionally, dys-regulation of miR-149-5p and IL-6 expression in individuals with CKD was observed. miR-149-5p down-regulation and IL-6 over-expression pointed toward the potential role of these two molecules in the pathogenesis of CKD.
Conclusion: The computational techniques utilized explain miR-149-5p’s role as a diagnostic, predictive, and potentially effective therapeutic target for CKD. Moreover, these findings contribute to a better understanding of CKD, along with miR-149-5p’s role in developing novel treatments for this disease.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
