Association between SORT1/CELSR2/PSRC1 rs646776 polymorphism and statin-affected plasma lipid levels
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v10i12.853Keywords:
statin, lipids, single nucleotide polymorphism, CELSR2, PSRC1, SORT1Abstract
Introduction: Statins are frequently prescribed for patients with hyperlipidemia to prevent cardiovascular disease, however, there is an inter-individual variability in their efficacy due to many factors, including genetic polymorphism. This study aimed to determine the association between single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the gene cluster SORT1-CELSR2-PSRC1 (rs646776) and lipid profiles in a subset of statin users in Malaysia.
Methods: In total, 122 statin-treated patients were recruited in this cross-sectional study. Genomic DNA from whole blood samples (3 mL) was extracted and genotyped using amplification-refractory mutation system-polymerase chain reaction (ARMS-PCR) for the rs646776 polymorphism. The association between the SNP and statin-related lipid profile changes was evaluated using a dominant genetic model (AA vs. GA + GG genotypes).
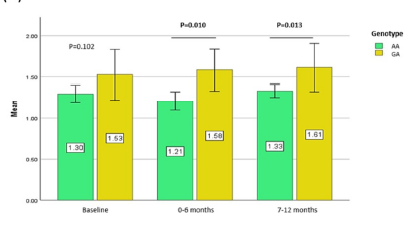
Results: The minor allele frequency of the rs646776 was 0.08 and the allele frequency of each genotype was in the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (P = 0.6149). Variant allele carriers of rs646776 showed higher (P < 0.05) high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels after statin treatment in females but not in males. Conversely, AA genotypes were linked to a significant decrease in total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (P < 0.01).
Conclusion: Our study provides the first frequency data for PSRC1/CELSR2/SORT1 rs646776 in the Southeast Asian region and further confirms the SNP association with improved HDL-C levels, especially in females using statins. The findings warrant further replication studies to validate the SNP association among different ethnicities in Asia.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
