DNA promoter methylation of cancer-associated genes in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v11i1.861Keywords:
DNA methylation, cancer associated genes, head and neck squamous cell carcinomaAbstract
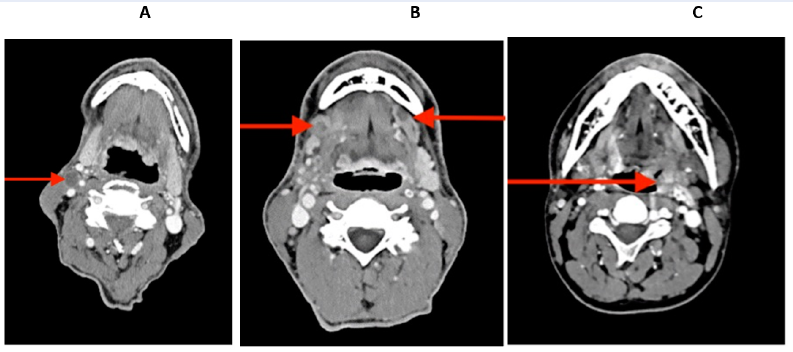
Introduction: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is the sixth most common cancer in the world. Abnormal methylation can be one reason for this cancer. This study aimed to investigate the DNA promotor methylation status of cancer-associated genes (ATM, APC, CDO1, RB1, TP53, and WIF1) in patients with HNSCC.
Methods: Bisulfite conversion and methylation-sensitive high-resolution melting were used to analyze the DNA methylation levels in normal and tumor tissues in 44 patients.
Results: Significant differences in DNA methylation were observed between tumor and normal tissues for CDO1 and WIF1 genes in all subjects and subgroups (p < 0.05). In the T3 subgroup, a significant correlation was found between CDO1 gene methylation and age in normal tissue. The same correlation was detected for the WIF1 gene methylation in tumor tissue samples in the subgroup with T3 and normal tissue samples in the subgroup with T4 (p < 0.05). In all genes, no significant differences were found between the patient subgroups (T2, T3, T4 stage, primary/recurrent lesion, non-keratinizing/keratinizing SCC, age before/after 50, and smokers/non-smokers).
Conclusion: Changes in the expressions of CDO1 and WIF1 genes can affect the mechanisms of the occurrence and development of HNSCC. Methylation in the ATM, APC, RB1, and TP53 genes is not specific to HNSCC.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
