First report of chronic portal vein thrombosis successfully managed with splenectomy and long-term direct oral anticoagulants
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v11i2.866Keywords:
non-cirrhotic portal hypertension, portal vein thrombosis, splenectomy, direct oral anticoagulantsAbstract
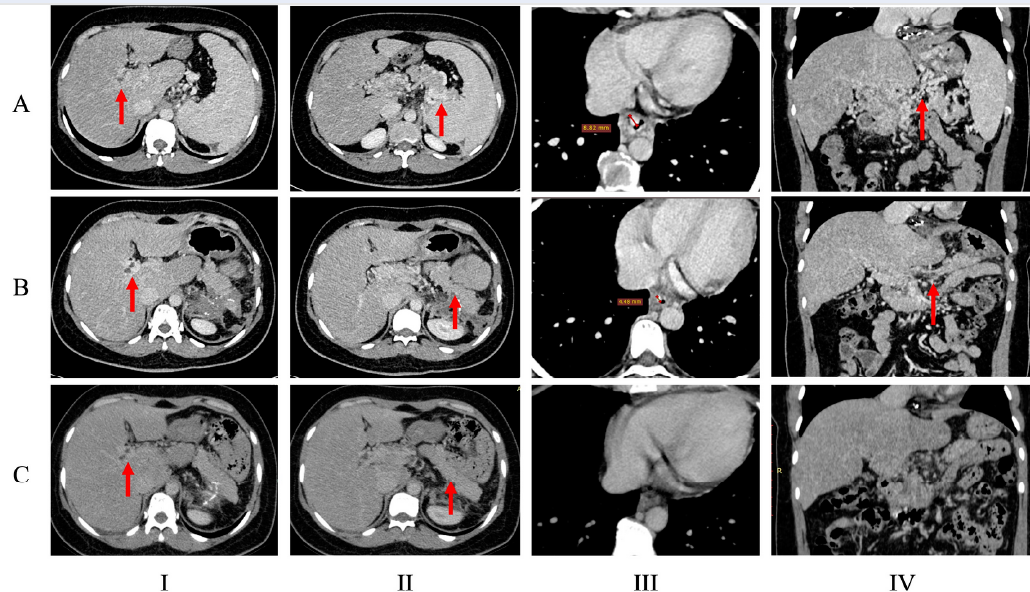
We report a rare case of portal vein thrombosis (PVT) secondary to idiopathic hypercoagulability leading to non-cirrhotic portal hypertension and cavernous transformation. The patient had a history of acute PVT and superior mesenteric vein thrombosis, which was initially managed successfully with anticoagulation therapy. However, the discontinuation of treatment precipitated a transition to chronic PVT and subsequent cavernous transformation. This condition manifested clinically as esophageal and gastric varices, posing a significant bleeding risk. Attempts to mitigate portal hypertension through medical management and endoscopic interventions had limited success. The anatomical complexities presented an insurmountable challenge to transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) placement, and thus alternative treatment strategies were considered. A splenectomy markedly improved the patient's condition. Over a 2-year follow-up period, with the aid of direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), the patient remained stable; further endoscopic procedures were not required, and the patient did not experience a recurrence of thromboembolic or hemorrhagic events. This case underscores the complexity of PVT management and highlights the need for individualized treatment approaches in the face of anatomical and therapeutic challenges.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
