Autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells transplantation showed potential benefits for type 2 diabetes mellitus Filipino patients: a case series
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v11i4.878Keywords:
type-2 diabetes, stem cell therapy, bone marrow-derived stem cell, HbA1cAbstract
Introduction: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a serious metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia and insulin resistance. Long-standing T2DM may lead to various macro- and microvascular complications such as diabetic nephropathy, neuropathy, and retinopathy. Currently available treatments for T2DM target high plasma glucose levels but do not address T2DM-associated complications. In this report, the therapeutic application of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) transplantation in improving diabetic blood monitoring parameters among selected T2DM patients was investigated.
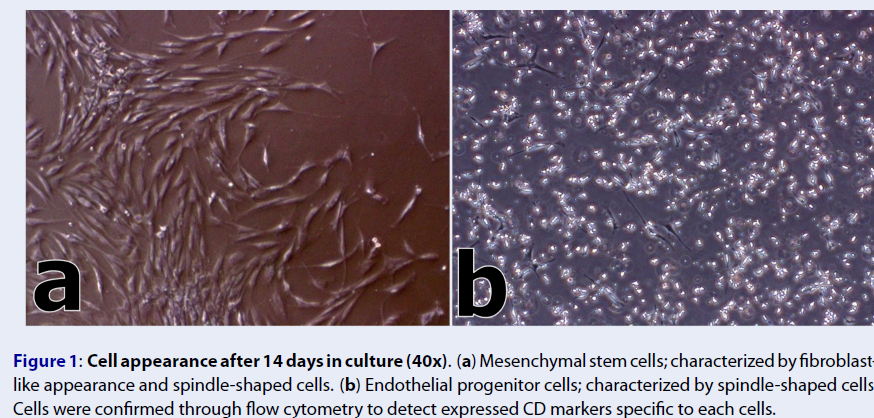
Methods: Five Filipino patients with T2DM diagnosed for more than five years agreed to participate in the autologous bone marrow-derived stem cell transplantation. Five milliliters (mL) per kilogram (kg) of bone marrow was collected from the patients following standard procedures, and bone marrow-derived stem cells underwent quantification, genetic typing, microbial analysis, and quality control before being infused into the patients. MSCs and EPCs were intravenously transfused into the patients once a month for 6 months. Fasting blood glucose (FBG), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and creatinine (CREA) levels were recorded pre- and post-stem cell transplantation.
Results: The findings of the study revealed that the administration of autologous bone marrow-derived stem cells showed no adverse effects and improved or controlled the blood monitoring levels in most patients. Four out of five patients showed a reduction in their BUN (mean reduction = 2.246) and HbA1c (mean reduction = 0.74%) and maintained their creatinine levels within the normal range following the 6 months of infusion. Meanwhile, three out of five patients showed a decrease in FBG levels (mean reduction = 1.484 mmol/L).
Conclusion: This preliminary report suggests the potential of autologous bone marrow-derived stem cell transplantation for the treatment and management of T2DM. Future studies may focus on examining other parameters such as C-peptide levels and evaluate the efficacy and safety of autologous MSCs and EPCs in the long-term management of T2DM.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
