In silico identification and gene expression of miR-148a-5p and IL-6 in hypothyroid patient blood samples
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v11i5.884Keywords:
Hypothyroidism, microRNA-148a-5p, Interleukin-6, gene expression, treatment, biomarker, health, diagnosisAbstract
Background: Hypothyroidism, marked by a deficiency in thyroid hormone levels, is a common condition with varying clinical presentations. The diagnosis primarily relies on statistical reference ranges of biochemical parameters, which remains a topic of contention. While manageable, untreated cases can lead to serious consequences. MicroRNAs, small non-coding RNAs, have been implicated in hypothyroidism and other diseases, underscoring their significant role in pathophysiology.
Methods: The study describes the bioinformatics techniques utilized to identify miR-148a-5p and to determine its secondary structure in hypothyroidism using databases such as NCBI, miRbase, TargetScan, and RNAfold. For clinical validation, blood samples from individuals with hypothyroidism and normal controls were collected, RNA was extracted, and reverse transcription was performed. The expression levels of RNA and IL-6 were quantified, and statistical analysis was conducted.
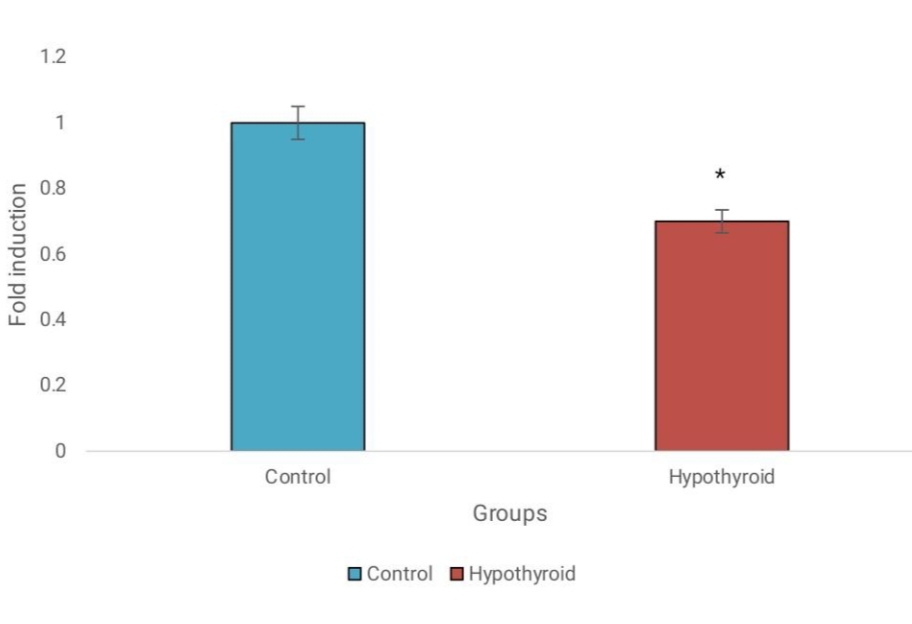
Results: Examination of the secondary structure reveals that hsa-miR-148a-5p has a minimum free energy of -27.90 kcal/mol. Consequently, our findings indicate dysregulation of miR-148a-5p and IL-6 expression in patients with hypothyroidism. There is upregulation of IL-6 and downregulation of miR-148a-5p, suggesting potential roles for these molecules in the pathogenesis of hypothyroidism.
Conclusion: The computational analysis suggests that miR-148a-5p is a promising diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic target for hypothyroidism. Based on the data presented in the study, the decreased expression of miR-148a-5p and elevated levels of IL-6 in patients with hypothyroidism suggest potential roles for these molecules in the pathogenesis of hypothyroidism. Further research is warranted to comprehensively understand dysregulation at the level of miR-148a-5p and its impact on IL-6 pathways in hypothyroidism.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
