Study on gene expression of IL-17A in eutopic and ectopic tissue sample of endometriosis patients and comparison with control group
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v11i6.894Keywords:
endometriosis, IL-17A, Th17 lymphocytes, inflammatoryAbstract
Introduction: The growth of endometrial tissue beyond the uterine cavity characterizes endometriosis, a chronic inflammatory disease. IL-17A, along with other immune mediators and a myriad of immune cells including Th17 lymphocytes and macrophages, are more prevalent in the peritoneal fluid of patients with endometriosis. IL–17A facilitates the implantation of endometrial tissue in ectopic locations by inducing growth factors and inflammatory cytokines from other immune cells. This work focuses on the levels of IL-17A gene expression in tissue samples from patient and control groups, as prior research has not extensively covered the gene expression of inflammatory mediators in tissue samples.
Methods: This study is both experimental and case-control in nature. Tissue samples were collected from 32 women undergoing laparoscopy at Yazd Shahid Sadoughi Hospital. The samples were divided into two groups: 16 patients with endometriosis and 16 healthy individuals. Within the patient group, there were two types of samples: eutopic and ectopic. The expression of IL-17A was assessed with RT-qPCR.
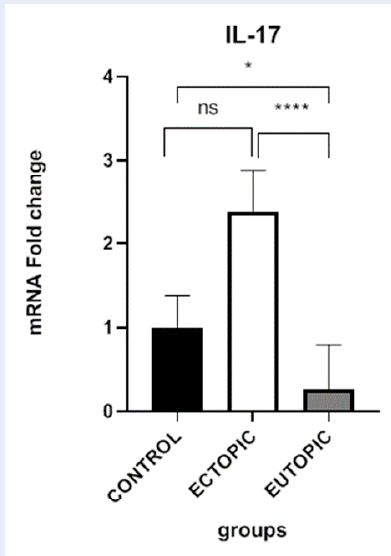
Results: RT-qPCR results showed a significant difference in IL-17A gene expression between ectopic lesions and eutopic samples from endometriosis patients (P value < 0.0001). Additionally, there was a significant increase in gene expression in eutopic samples from endometriosis patients compared to control samples (P value = 0.0176).
Conclusion: This study confirms the crucial involvement of inflammatory mediators like IL-17A in endometriosis through molecular findings in tissue samples, reflecting the elevated IL-17A content in the eutopic endometrium and ectopic lesions of endometriosis patients.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
