Disparity and trends in the incidence and mortality of lung cancer in the world
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v5i6.447Keywords:
Incidence, Lung Cancer, Mortality, the world, TrendAbstract
Background: Lung Cancer (LC) is one of the most common cancers in the international arena. The aim of this study was to investigate the geographical distribution of LC incidence and mortality in the world in 2012, as well as the trend of incidence and mortality of LC during 1975 to 2010 based on the gender.
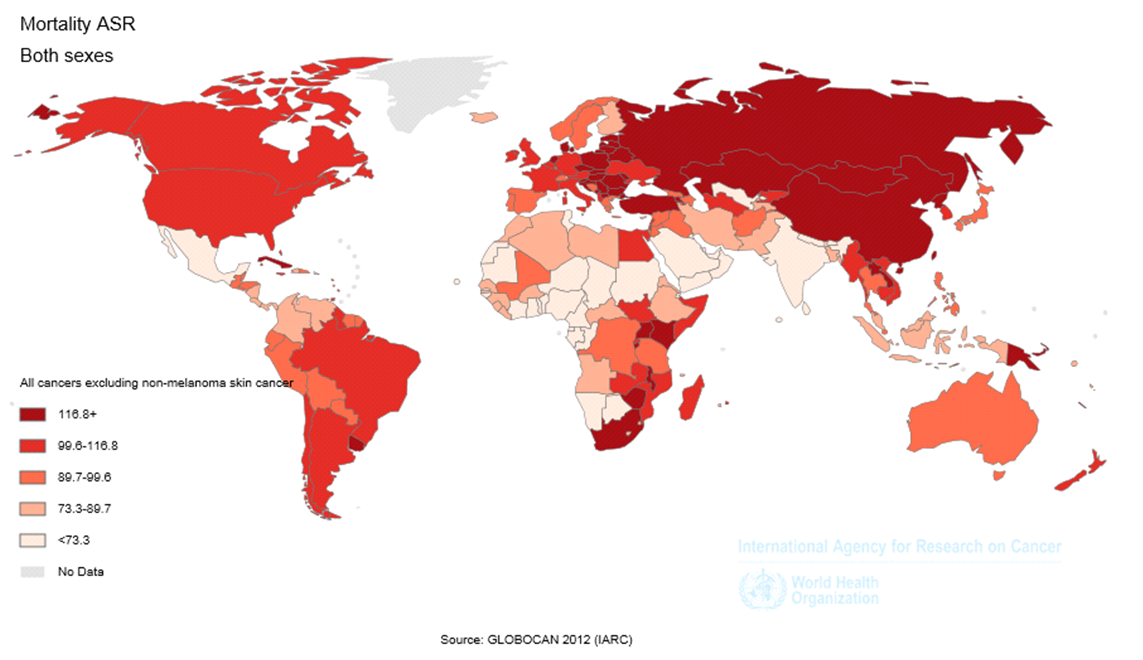
Methods: In the present study, we extracted the information on the incidence and mortality of LC in 184 countries from the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) (Project GLOBOCAN, 2012). The present study categorized and presented the information on the Age-Standardized Incidence Rate (ASIR) and Age Standardized Mortality Rate (ASMR) of LC based on the continents, world regions based on the development level and Human Development Index (HDI). ASIR and ASMR of LC expressed per 100,000 people.
Results: The highest ASIR and ASMR of LC occurred in North America (ASIR=38.3 and ASMR=28.6), more developed regions (ASIR=30.8 and ASMR=24.2), and the WPRO region of the WHO (ASIR=32.8 and ASMR=28.5), and those regions with very high HDI (ASIR=31 and ASMR=23.9). Furthermore, the lowest ASIR and ASMR of LC occurred in Africa (ASIR=5 and ASMR=4.5), the less developed regions (ASIR=20 and ASMR=18), the AFRO region (ASIR=3.9 and ASMR=3.5), and regions with low HDI (ASIR=5.4 and ASMR=4.8).
Conclusion: The highest ASIR and ASMR of LC occurred in North America, more developed regions, and the WPRO region of the WHO, and those regions with very high HDI. Most regions of the world had decreasing incidence and mortality of LC in men and increasing trend in women.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
