Evaluation of the role of whey with dodder oxymel on mild to moderate psoriasis: A double-blind, randomized controlled trial
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v5i8.470Keywords:
Complementary and alternative medicine, Persian medicine, Psoriasis, Quality of life, Whey with dodder oxymelAbstract
Introduction: Psoriasis is a common chronic inflammatory disease that affects the physical, mental and sexual well-being of patients. Numerous side effects of different treatments and inadequate response to medications have resulted in pursuit of ideal treatment with low toxicity in low burden psoriasis hence complementary medicine. This study aims to evaluate the effects of whey with dodder oxymel on mild to moderate psoriatic skin lesions.
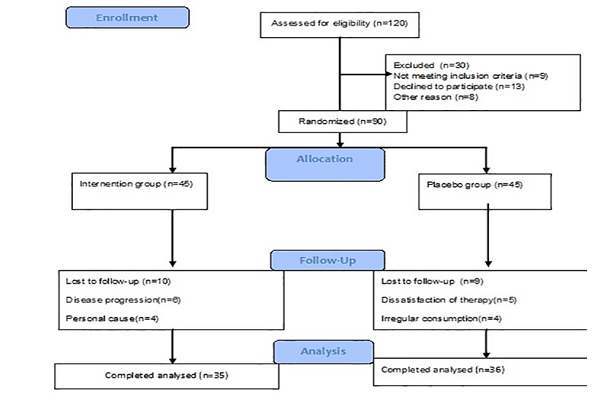
Methods: A 12-week double-blind, randomized, controlled, clinical trial was designed. Ninety psoriatic patients participated in the intervention. Drug and placebo were randomly assigned to two groups identically (whey with dodder oxymel and lactose). Patients were visited twice by a dermatologist. Their clinical responses were evaluated using the Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI), the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and the Body Surface Area (BSA).
Results: After 12 weeks, in the intragroup analysis, the mean PASI score (P-value < 0.001) and BSA (P-value = 0.004) decreased in the intervention group. The mean VAS score (P-value < 0.001) and DLQI (Pvalue < 0.001) in both groups decreased. However, this decrease was much higher in the intervention group. In the intergroup analysis, 70% of patients reported improvement in PASI score (P-value < 0.001), the 88% improvement in quality of life (P-value < 0.001) and pruritus intensity (VAS) (P-value < 0.001), and the 54% reduction was detected in the area of lesions (BSA) (P-value = 0.001) as compared to the placebo group.
Conclusion: It appears that whey with dodder oxymel would improve psoriasis conditions and it can increase patients’ quality of life.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
