Determination of electrophysiological properties of human monocytes and THP-1 cells by dielectrophoresis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v6i3.527Keywords:
Dielectrophoresis, Lab on a Chip, Monocytes, THP-1 cellsAbstract
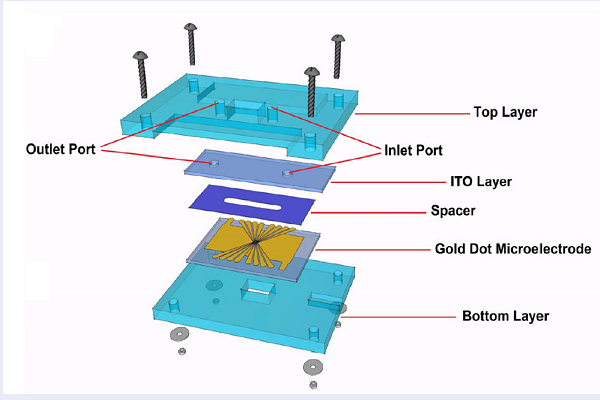
Introduction: Dielectrophoresis (DEP) is based on polarization and bioparticle movement in applied electric fields. Each type of cells has its own electrical properties within the DEP spectra and undergoes significant changes in direction of frequency following an increase of an applied nonuniform alternating current (AC) electric field. Therefore, DEP can be an effective technique for characterization and separation of different cells. The goal of the current study was to determine the electrophysiological properties of human monocytes and a human monocytic cell line originated from an acute monocytic leukemia patient (THP-1), using a lab on a chip (LOC) device that utilised microarray dot electrodes.
Methods: Ten microliters of human monocytes isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells and highly confluent THP-1 cells were diluted in DEP medium and added to the spacer of the LOC device. Subsequently, the AC signal in the range of 10 kHz to 2 MHz was supplied to the LOC device, and the dynamic behaviours of monocytes and THP-1 cells due to the DEP force were observed. Images were captured and analyzed using MATLAB software.
Results: Microscopic visualization showed that THP-1 cells were physically larger than human monocytes. The dielectric parameters (radius, diameter, and conductivity and permittivity of the cytoplasm and membrane) were greater for THP-1 cells compared to monocytes. The cross-over frequencies for THP-1 cells and monocytes were respectively 66 kHz and 280 kHz.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the DEP spectra reflected the morphological differences between monocytes and THP-1 cells. The dielectric properties for each type of cells can be used as the criteria in the development of DEP-based characterization assays.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
