Physiological and biochemical studies on the protective effect of Ficus carica leaf extract, vitamin C or their combination on liver toxicity induced by lead acetate in male rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v5i10.488Keywords:
Antioxidants, Ficus carica, Hepatotoxicity, Lead, Vitamin CAbstract
Introduction: Lead is an environmental contaminant, which is toxic to organ systems in human and other animals. The present study investigated the possible protective role of Ficus carica leaf extract, vitamin C or the combined treatment in lead acetate-induced hepatotoxicity.
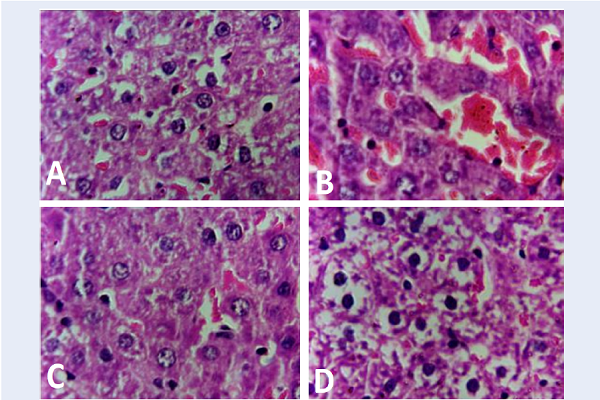
Methods: One hundred and twenty-six adult male albino rats were divided into seven groups (n = 18). G1 (control group) received distilled water. G2 (lead acetate group) received lead acetate at a daily dose of 20 mg/kg body weight by gastric gavage. G3 (Ficus carica group) received Ficus carica leaves extract at a daily dose of 200 mg/kg body weight by gastric gavage. G4 (Ficus and lead group) received Ficus carica leaves extract followed by lead acetate after 20 minutes. G5 (vitamin C group) received vitamin C at a daily dose of 200 mg/kg body weight by gastric gavage, G6 (vitamin c and lead group) received vitamin C followed by lead acetate after 20 minutes. And, G7 (Ficus, vitamin C, and lead group) received Ficus carica leaves extract and vitamin C followed by lead acetate after 20 minutes. The treatment extended for six weeks, blood and specimens were collected at a 2-week interval. Serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), total protein (TP), direct bilirubin (DB), lipid peroxidation biomarker (Malondialdehyde (MDA)), antioxidants enzymes (Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and reduced glutathione (GSH)) in liver tissue and histopathological changes in liver were investigated.
Results: Lead acetate caused significant increases in AST, ALT, ALP, DB and MDA levels. In addition, TP and level of SOD and GSH significantly decreased compared to the control group. The pre-treatment with the combination of Ficus carica and vitamin C improved liver parameters, the level of antioxidant enzymes as well as histopathological changes.
Conclusion: The combination of Ficus carica leaf extract and vitamin C had a remarkable protective action against lead acetate induced- oxidative damage in rats.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
