Therapeutic potential of curcumin against lead-induced toxicity: A review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v6i3.528Keywords:
Anti-inflammatory, Antioxidant, Curcumin, Lead-induced toxicity, Oxidative stress, Reactive oxygen speciesAbstract
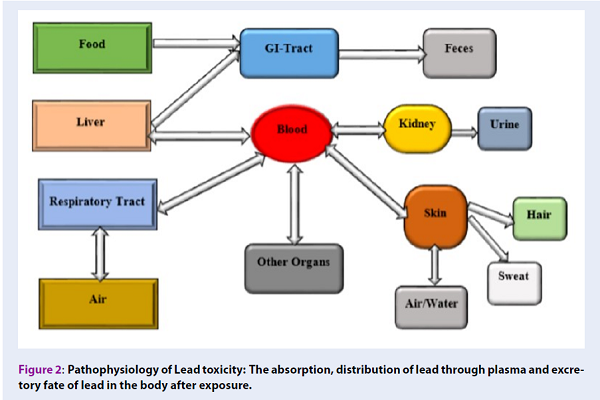
Lead poisoning causes numerous clinical implications in almost all organs, with the brain, liver, and kidneys serving as the primary targets due to the abundant presence of mitochondria. Curcumin is one of the most potent constituents of Curcuma longa, which is lipophilic, phenolic and water insoluble. Curcumin is a strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent in the treatments of neurodegenerative disease, cardiovascular, renal, and liver diseases, with a potential anticancer mechanism in a few clinical and experimental trials. This review will focus on the health impact of lead-induced toxicity in different organ-systems, which occurs as result of increased oxidative stress through the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) and will discuss the therapeutic potential of curcumin against lead-induced toxicity in both human and animals.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
