Evaluation of butyrylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase activity in serum and saliva of myocardial infarction patients
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v5i10.491Keywords:
Acetylcholinesterase, Butyrylcholinesterase, Myocardial infarctionAbstract
Background: Myocardial infarction (MI) is one of the most common cardiovascular diseases. It accounts for about half of death cases in Iran. The objective of this study was to compare the activity of butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) enzymes in serum and saliva of the MI patients compared to the healthy controls.
Methods: Serum and salivary BChE and AChE levels were measured immediately following MI, and then 24 and 72 hours later. Four mL of blood and two mL saliva were collected for this purpose. These measurements were also collected in 30 healthy controls. The enzymes were assayed using spectrophotometry.
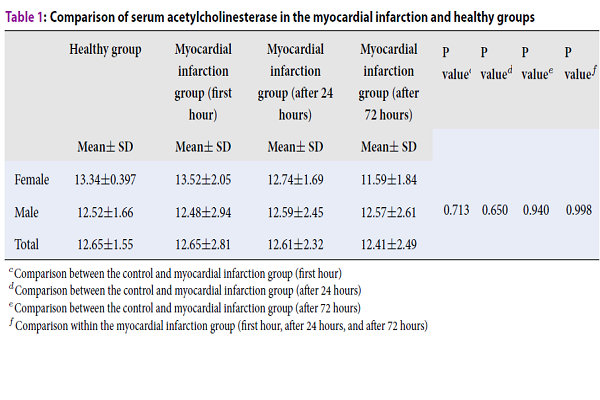
Results: The activity of salivary AChE in the MI patients was lower than that of the healthy controls right after, 24 hours, and 72 hours following MI. However, serum AChE did not show a significant difference between the two groups. The activity of serum BChE in the MI patients was lower than that of the healthy controls right after, 24 hours, and 72 hours following MI. However, salivary BChE did not show a significant difference between the two groups.
Conclusion: The activity of salivary AChE decreased in the MI patients compared to the healthy controls, which can be a marker to diagnose MI in the future.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
