Toxicological evaluation of the nicotine on CA1 and protective effects of curcuma longa: An experimental study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v6i9.565Keywords:
CA1, Curcuma longa, NicotineAbstract
Introduction: Nicotine is the most important alkaloid compound in tobacco and is a major risk factor in the development of functional disorders of several organ systems. Some plants produce Curcuma longa (curcumin), which has antioxidant and neuro-protective properties.
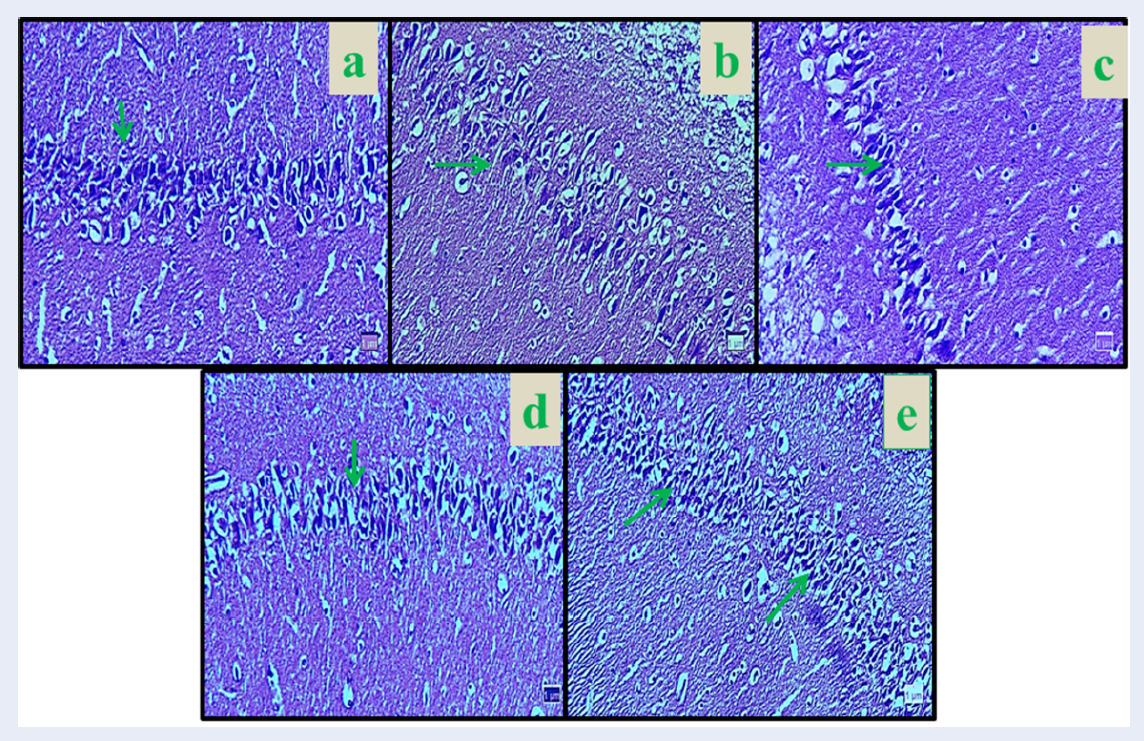
Methods: This study was designed to evaluate the therapeutic effects of curcumin against nicotine injury on the hippocampus CA1 region of rats. In this study, 48 male rats were randomly assigned to eight groups: Normal control (saline) group, Nicotine control group (0.5 mg/kg); Curcumin groups (10, 30, and 60 mg/kg) and Nicotine + Curcumin groups (10, 30, and 60 mg/kg). Treatments were administered intra-peritoneally daily for 28 days. Golgi staining technique investigated the number of dendritic spines. Cresyl violet staining method was used to determine the number of neurons in the hippocampal region CA1. Griess technique was assessed to determine serum nitrite oxide levels. Also, the ferric reducing/antioxidant power (FRAP) method was applied to determine the total antioxidant capacity.
Results: Nicotine administration significantly increased the nitrite oxide level and decreased total antioxidant capacity. The number of neuronal dendritic spines, as well as neurons per se, also decreased, compared to the control group (p < 0.01). In all the members of the Curcumin and Nicotine + Curcumin groups, the number of neurons, neuronal dendritic spines and total antioxidant capacity increased significantly compared to the nicotine control group, while nitrite oxide level decreased significantly compared to the nicotine control group (p < 0.01).
Conclusions: It seems that Curcumin administration improved hippocampal CA1 region injury in rats caused by Nicotine.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright The Author(s) 2017. This article is published with open access by BioMedPress. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC-BY 4.0) which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
